The productivity of the Indian Parliament has seen a significant decline in recent years, marked by fewer sitting days and a reduction in the number of bills passed. The 17th Lok Sabha is on track to be the shortest full-term Lok Sabha since 1952. Political polarisation, inadequate preparation, and a lack of diversity contribute to this trend. Understanding these issues is crucial for enhancing the Parliament’s effectiveness.
Addressing Diminishing Productivity in the Indian Parliament: Causes and Remedies
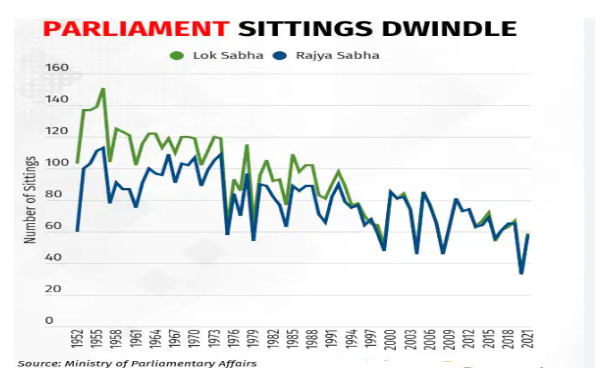
Decline of Parliament Productivity in Recent Years
- Overview of the 17th Lok Sabha’s Sitting Days: The 17th Lok Sabha, in its penultimate year, has operated for 230 sitting days.
- Sitting Days of the 16th Lok Sabha: Among Lok Sabhas completing a full five-year term, the 16th Lok Sabha recorded the fewest sitting days (331).
- Projected Performance of the 17th Lok Sabha: With an average of 58 sitting days per year and one year left, it’s improbable for the 17th Lok Sabha to exceed the 331-day mark.
- If this occurs, it would be the shortest full-term Lok Sabha since 1952.
- 17th Lok Sabha was the first to go an entire term without a Deputy Speaker.
- Legislative Productivity Trends: According to PRS Legislative Research data, the number of bills passed by the Lok Sabha has decreased over the years.
- Legislative Output of the Lok Sabhas: In the 17th Lok Sabha (2014-2019), 221 bills were passed, compared to 248 bills in the15th Lok Sabha (2009-2014).
- Impact of Disruptions on Legislative Efficiency: Analysis by IndiaSpend reveals that the 16th Lok Sabha lost 29% of its scheduled time due to disruptions, while the 17th Lok Sabha has lost 48% of its scheduled time to date.
- Decline in Private Members’ Bills: Private Members’ Bills, introduced by non-government MPs.
- 729 Private Members’ Bills (PMBs) were introduced in the 17th Lok Sabha, which is higher than all previous Lok Sabhas, except the 16th
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Factors Contributing to Diminishing Productivity in the Indian Parliament
The diminishing productivity of the Indian Parliament can be attributed to various factors:
- Political Polarization and Confrontational Politics:
- Frequent disruptions in the House.
- Protests, sloganeering, and walkouts by MPs.
- Impedes smooth Parliamentary functioning.
- Lack of Adequate Preparation and Deliberation:
- Rushed passage of bills without thorough discussions.
- Results in inadequate scrutiny and oversight.
- This leads to poorly drafted legislation causing delays and controversies.
- Strong Anti-defection measures:
- MPs always have to tow party-line.
- MPs turn into mouthpieces of respective parties instead of being the voice of the people.
- Weak Committee System:
- Ineffective scrutiny of bills due to a weak committee system.
- Committees play a crucial role in research and stakeholder consultations.
- Bypassing committees hampers the legislative process.
- Absence of Diversity in Parliament:
- Significant underrepresentation of marginalized groups.
- Lack of diverse voices and perspectives.
- Legislation may not reflect the needs of all sections of society.
Ways to Enhance Parliamentary Productivity in India
-
- Promote Constructive and Consensus-based Politics:
- Encourage collaboration among members from different parties.
- Reduce disruptions in the House for more efficient functioning.
- Improve Preparation and Scrutiny of Bills:
- Establish a robust committee system for in-depth research.
- Facilitate consultations with stakeholders for well-drafted bills.
- Ensure thorough scrutiny and adequate debate in Parliament.
- Promote Constructive and Consensus-based Politics:
- Enhance Diversity and Representation:
-
-
- Increase representation of marginalized groups (women, Dalits, religious minorities).
- Ensure diverse voices are heard, reflecting societal needs in legislation.
-
- Leverage Technology for Efficiency:
-
-
- Implement electronic voting systems for streamlined processes.
- Enable remote attendance for members to reduce disruptions.
- Enhance digital communication channels for efficient operations.
-
- Focus on Capacity-building and Training:
-
- Provide training for MPs in legislative drafting and public speaking.
- Enhance skills for effective committee work.
- Empower Parliamentarians to contribute to better legislative outcomes.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
Improving the productivity of the Indian Parliament requires a multifaceted approach, including fostering collaboration among parties and enhancing bill preparation.
- Increasing representation of marginalized groups and leveraging technology can also play a vital role.
- By addressing these challenges, Parliament can strengthen democratic governance and better serve the needs of all citizens.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Indian Parliament | 2024 Lok Sabha Election Results Live Updates |
| Private Members’ Bill | Anti-Defection Law |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









