In the Presidential system of government, the executive is not responsible to the legislature for its policies and acts and is Constitutionally independent of the legislature in respect of its term of office. This system of government is also known as the non-responsible or fixed executive system of government. The system is prevalent in the USA, Brazil, Russia, etc.
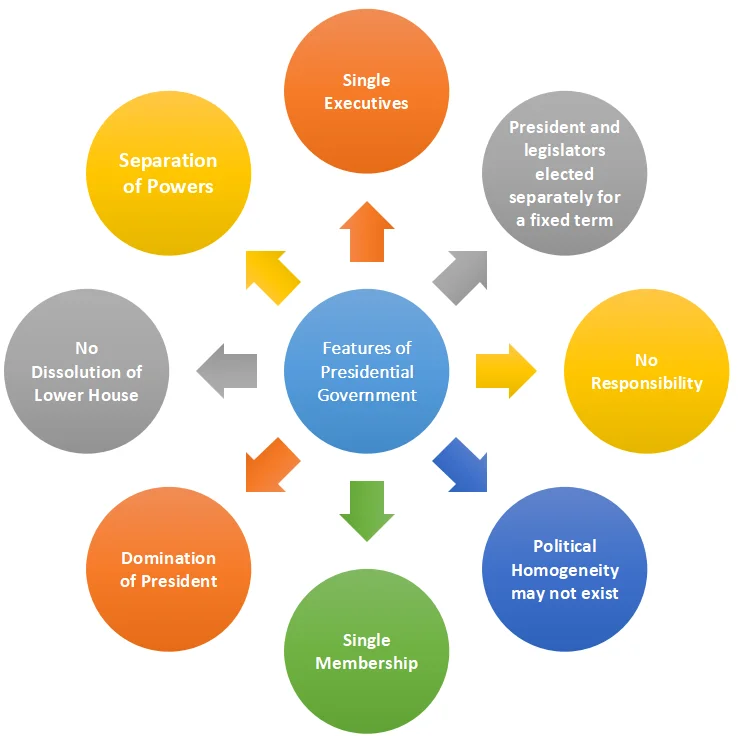
Features of Presidential Government
Single Executive: The President is both the head of the State and the head of Government.
- Fixed Term: The President is elected by an electoral college for a fixed tenure.
- He cannot be removed by the Legislature except by impeachment for a grave unconstitutional act.
- Domination of President: The President governs with the help of a cabinet or a smaller body called ‘Kitchen Cabinet’ which is only an advisory body and consists of non-elected departmental secretaries.
- These members are selected and appointed by him, are responsible only to him, and can be removed by him at any time.
- Non-Responsibility: The President and his secretaries are not responsible to the legislature for their acts.
- No Dissolution of Lower House: The President cannot dissolve the House of Representatives.
- Separation of Power: The doctrine of separation of powers is the basis of the Presidential system where the legislative, executive, and judiciary powers are separated and vested in the three organs of the government.
- Single Membership: The President and his secretaries neither possess membership in the Congress (legislature) nor attend its sessions.
- Political Homogeneity may not exist: The Presidential system does not adhere to the principle of homogeneity in the cabinet as members can be from different political parties.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Parliamentary System | Presidential System | |
| Merits |
|
|
| Demerits |
|
|
Should We Adopt The Presidential System?
Parliamentary vs. Presidential System: The question of whether to persist with the parliamentary system or transition to the Presidential system has been a subject of discussion and debate in our country since the 1970s.

-
Arguments in Favour of the Presidential System
-
-
- Stable Executive: It establishes a stable executive that does not depend upon the uncertain will of the legislature, especially in the case of coalition governments.
- Preference to ability: The President can appoint anyone as secretary, equivalent to a minister.
- Posts are not limited to those who are electable rather than those who are able.
- Effective Checks and Balances: The system prevents abuse of power by allowing the two structures – the presidency and the legislature, to monitor and check each other.
- Swift Decision-making: The Presidential system of government provides quick decision-making.
-
-
Argument Against the Presidential System
-
- Lack of Cooperation: It fails to ensure cooperation between legislature and executive.
- Frequent conflicts between the lawmaker and the administrator may lead to deadlocks.
- Autocratic: The system centralises power in one individual, unlike the parliamentary system, where the Prime Minister is the first among equals in the parliamentary system.
- Giving authority to one individual, as in the Presidential system, is dangerous for democracy.
- Issue of Governance: If the legislature is dominated by the same party to which the President belongs, he may prevent any move from the legislature.
- Against the Basic Structure of the Constitution: Shifting to the Presidential system is not possible under our present Constitutional setup as the parliamentary form of government is part of the ‘basic structure’ doctrine propounded by the Supreme Court.
- Affecting Pluralism: India is a diverse country that cannot function without consensus-building.
- Lack of Cooperation: It fails to ensure cooperation between legislature and executive.
Is the Indian Polity increasingly transitioning towards Presidential form
Scholarly Perspectives: There is an opinion among scholars that India is witnessing increasing Presidentialization of its Parliamentary system in recent times.
-
Reasons for Concern
-
-
- Centralization of Executive Functions: Style of leadership is changing. It is alleged that the executive is becoming centralised in its functioning.
- Rise of Individual Leadership: According to critics, the executive decisions are being made by a few individuals rather than the cabinet/council of ministers.
- The system of elections is increasingly becoming centred around the cult of individual leadership.
- Decline in Parliamentary Accountability: The ability of parliament to hold the executive accountable has been decreasing due to weak opposition, frequent disruptions, etc.
- Appointment of Non-Elected Ministers: Appointment of people (like ex-bureaucrats, who have not contested direct elections) as ministers is similar to the Presidential system (spoils system)
-
- Arguments Against India Shifting to a Presidential System; However, the notion that India is shifting towards a Presidential system of government cannot said to be true because:
-
- Strong Parliamentary Tradition and Institutions: India has a strong parliamentary tradition and institutions like the supreme court to protect democratic parliamentary credentials.
- Basic Structure Doctrine: SC has declared a parliamentary form of government as part of the basic structure of the Constitution.
- Parliamentary Accountability: Parliament and its committees have held the executive accountable by raising questions, debating policy of executives and informing the public about various issues.
- Requirement for Ministers to Be MPs: Even when outsiders are given ministerial births, they must become members of Parliament within 6 months.
- Example: S. Jaishankar was nominated to RS.
- Maintaining Parliamentary System Despite Centralising Tendencies: Although certain centralising tendencies have been witnessed, it would be unwise to say that India is transitioning from a parliamentary to a presidential system.
- A strong majority in parliament has led to an apprehension of the presidential Prime Minister.
- However, apart from parliament, EC, judiciary, etc., strong civil society and media have been able to ensure that PM and CoM remain accountable to the parliament in general and LS in particular
Semi-Presidential
Overview: A Semi-Presidential system of government incorporates features from both Parliamentary and Presidential systems.

- Head of State and Government: In this system, the Head of the State is the President directly elected by the people, whilst the head of government is the Prime Minister nominated by the President but can be dismissed by the legislature.
- Example: France, Sri Lanka

Merits and Demerits of Semi-Presidential System
| Merits | Demerits |
|
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
The debate between adopting a Presidential or Parliamentary system in India hinges on stability, cooperation, and accountability.
- While the Presidential system offers stable and decisive governance, it risks centralizing power and reducing legislative cooperation. The Parliamentary system, despite potential instability, ensures executive accountability and broad representation.
- India’s strong democratic traditions and institutions, like the Supreme Court and Parliament, continue to support its Parliamentary framework, balancing central authority with diverse representation.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Legislative Procedure In State Legislature | President of India |
| India’s Parliamentary System | Supreme Court |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program










