In India, the recognition of political parties as national or state entities by the Election Commission plays a crucial role in the electoral process. This recognition is based on the parties’ poll performances and grants them various privileges, which are essential for their functioning. Unrecognized parties, on the other hand, are classified as registered unrecognized parties, lacking the benefits afforded to recognized parties.
Recognition of National and State Political Parties in India
Registration and Recognition of Political Parties by the Election Commission of India: Based on poll performances, the Election Commission of India registers political parties as national or state parties for elections and grants them recognition. Other parties are declared as registered unrecognized parties.
Need of recognition for Parties
- Right to certain privileges-
- Access to electoral rolls.
- Provision of time for political broadcasts on the state-owned television and radio stations.
- Allocation of the party symbols.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Allocation of Party Symbols-
|
Role of proposers and star campaigners
- Recognized Parties: They need only one proposer to file the nomination. They are allowed to have forty star campaigners during elections.
- Registered-Unrecognized Parties: They are allowed to have only twenty-star campaigners.
- The expenses of these star campaigners are not included in the election expenditure of the candidates.
Conditions for Recognition as a National Party
- A party is recognized as a national party upon fulfillment of any of the following conditions-
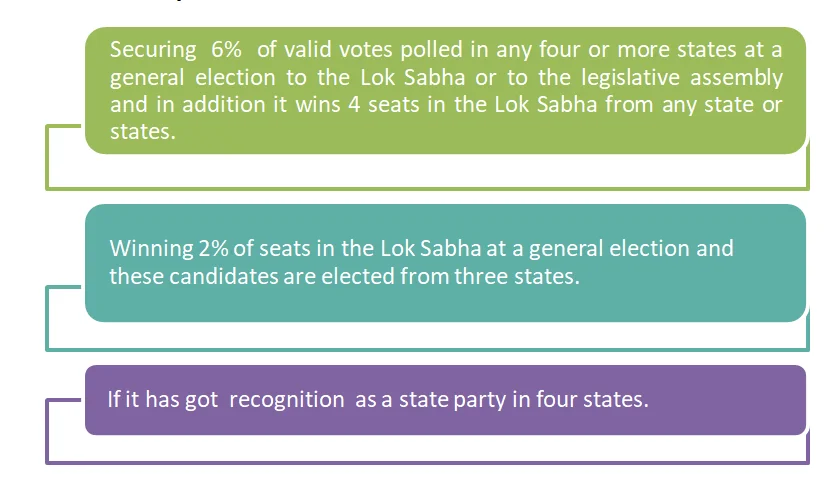
-
- At Present, current National Parties:
- Indian National Congress
- Bhartiya Janata Party
- Communist Party of India ( Marxist )
- Aam Aadmi Party
- Bahujan Samaj Party
- National Peoples Party
Conditions for Recognition as a State Party
- A party is recognized as a state party in a state if it fulfills any of the following criteria-
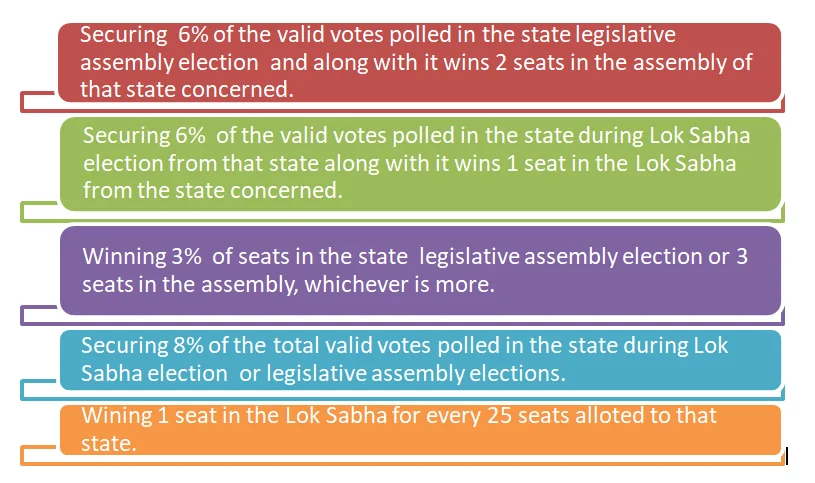
Necessity of Registration with the Election Commission of India
- Not Mandatory for All Associations: It is not required for every association to register with the Election Commission. Only those groups identifying as political parties and intending to utilize the provisions of Part IV-A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951, must register.
Benefits of Registration with the Election Commission of India
- Preference in Symbol Allotment: Candidates fielded by registered political parties receive priority in the allotment of free symbols compared to independent candidates.
- Potential for Recognition: Registered political parties can achieve recognition as a “State Party” or “National Party” by fulfilling the criteria set by the Election Commission in the Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order, 1968.
- Exclusive Symbol Allotment: A recognized State Party is entitled to exclusive use of its reserved symbol in the states where it is recognized, while a National Party can use its symbol throughout India.
- Simplified Nomination Process: Recognized parties only require one proposer to file nominations.
- Access to Electoral Rolls: Recognized parties receive two sets of electoral rolls free of cost.
- Broadcast and Telecast Facilities: Registered parties are eligible for broadcast and telecast facilities over Akashvani/Doordarshan during general elections.
Difference Between Registered Parties and Recognised Parties
| Aspect | Registered Parties | Recognised Parties |
| Definition |
|
|
| Requirements |
|
|
| Legal Benefits |
|
|
| Number of Parties |
|
|
| Purpose of Registration |
|
|
| Consequences of Registration |
|
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
Recognized parties have distinct advantages, such as exclusive symbols and simplified nomination processes, which enhance their electoral prospects.
- With currently six national parties and several state parties, recognition significantly influences their visibility and credibility in elections.
- Overall, the framework provided by the Election Commission supports a healthy democracy by promoting accountability and transparency within political parties.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Election Commission of India | Making Of The Indian Constitution |
| Indian National Congress: Formation and Debates | Indian Democracy |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









