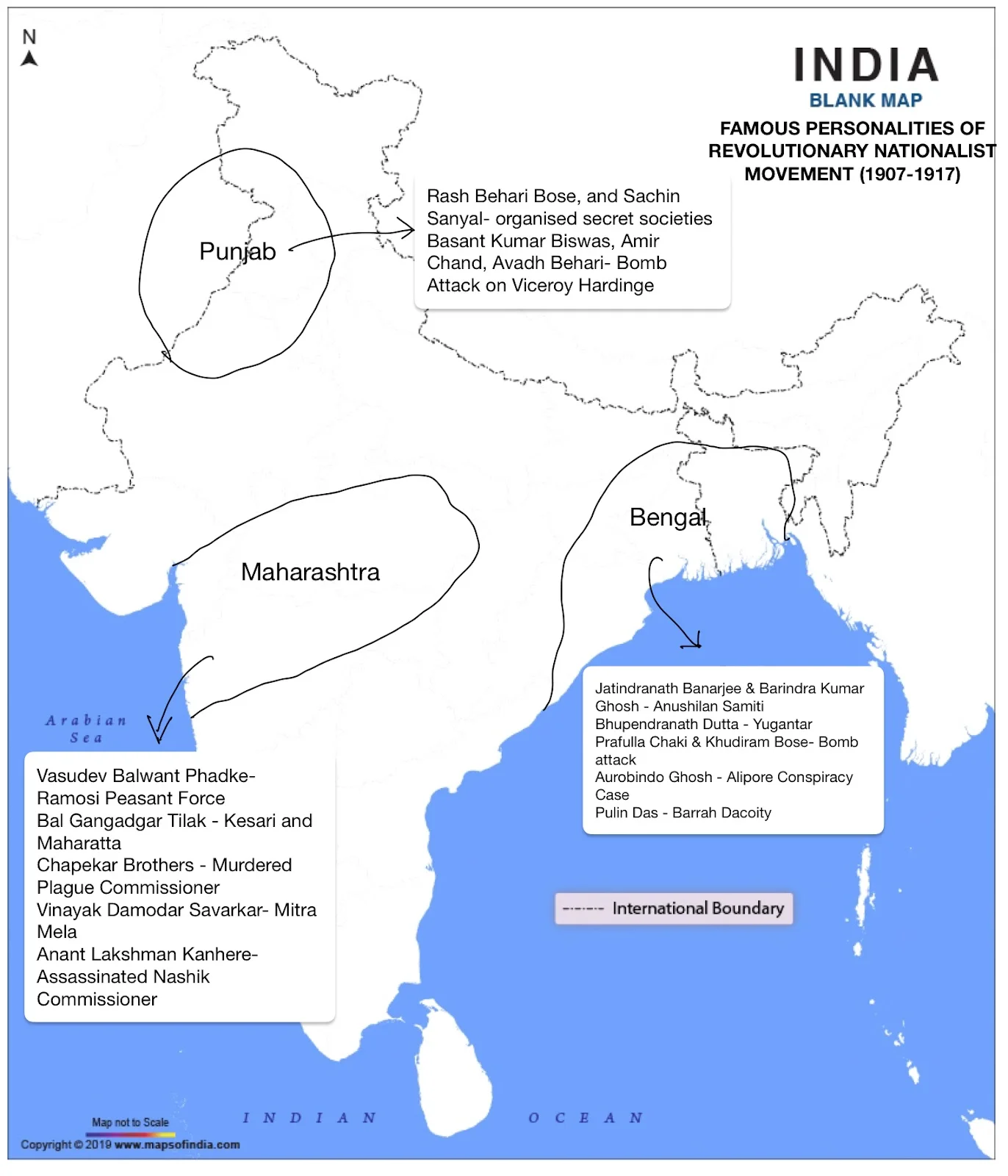
During the Early phase, revolutionary nationalism confined to India was in Bengal, Maharashtra, Punjab, U.P.Orissa, Biha, and Madras provinces, but it predominantly operated in major three regions Bengal, Maharashtra, and Punjab as these regions were more politically active than other parts of the country. Now let us study a brief survey of the revolutionary activities in different parts of India and abroad before and during the First World War.
Revolutionary Activities in Maharashtra
The revolutionary activities in Maharashtra during the British colonial period were marked by courageous individuals and groups who fought tirelessly for independence. These activities were led by popular personalities like Vasudev Balwant Phadke, Bal Gangadhar Tilak, and Savarkar, these revolutionaries sought to free the nation from British rule through armed uprisings, militant nationalism, and acts of defiance.
| YEAR | PERSONALITY | PLACE | WORK |
| 1879 | Vasudev Balwant Phadke | Maharashtra | The Ramosi Peasant Force aimed to eliminate British rule by inciting an armed uprising through acts of robbery. |
| 1890s | B.G Tilak | Maharashtra | Tilak advocated militant nationalism, by promoting the spirit of nationalism during Ganapati and Shivaji festivals and through his journals Kesari and Maharatta. |
| 1897 | Chapekar Brothers | Maharashtra | Murdered the Plague Commissioner of Poona, Rand, and Lt. Ayerst |
| 1899 | V. D Savarkar | Maharashtra | Savarkar organized Mitra Mela, a secret society that merged with Abhinav Bharat in 1904. |
| 1909 | Anant Laxman Kanhere | Nashik | The Collector of Nashik was assassinated. |
Major Activities
- Ramosi Peasant Force: The initial revolutionary activity in Maharashtra began with Vasudev Balwant Phadke’s formation of the Ramosi Peasant Force in 1879.
- Their objective was to eliminate British rule by inciting an armed uprising through acts of robbery.
- However, their efforts were swiftly suppressed.
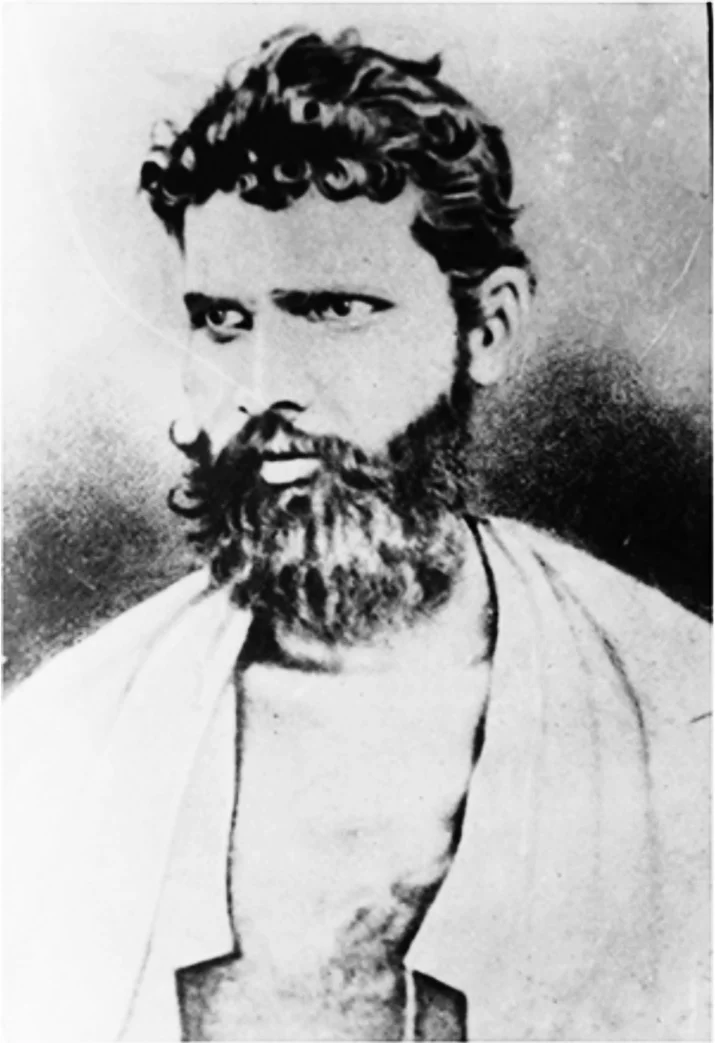

- Kesari and Maharatta: In the 1890s, Bal Gangadhar Tilak advocated militant nationalism, including the use of violence, by promoting the spirit of nationalism during Ganapati and Shivaji festivals and through his journals Kesari and Maharatta.
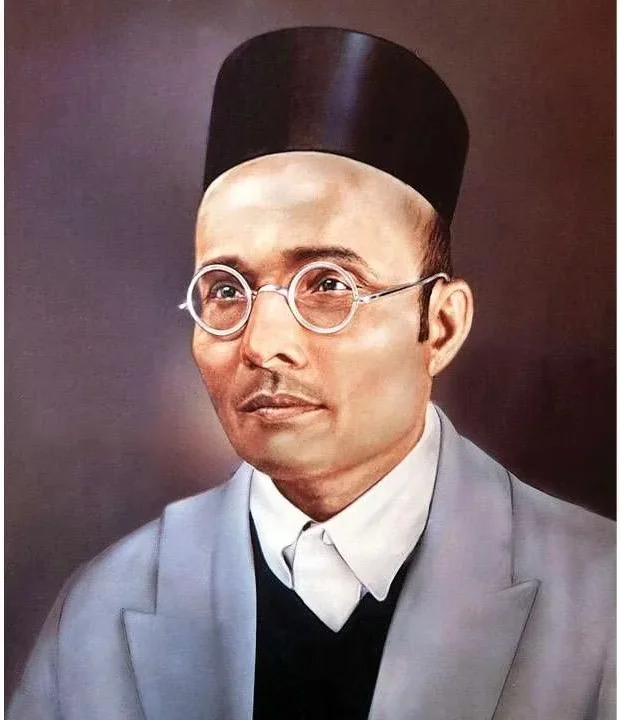

- Assassination of Rand: Two of his disciples, Damodar and Balkrishna Chapekar, assassinated the Plague Commissioner of Poona, Rand, and Lieutenant Ayerst in 1897.
- Abhinav Bharat and Nasik Conspiracy Case: Vinayak Damodar Savarkar and his brother organized Mitra Mela, a secret society, in 1899, which later merged with Abhinav Bharat (inspired by Mazzini’s ‘Young Italy’) in 1904.
- The cities of Nasik, Poona, and Bombay became centers for the manufacture of bombs.
- In 1909, A.M.T. Jackson, the Collector of Nashik, who was also a well-known Indologist, was assassinated by Anant Lakshman Kanhere, a member of Abhinav Bharat. It was discovered that this murder was part of a larger conspiracy aimed at overthrowing the British government in India through armed revolution.
- Role of Savarkar: Thirty-eight individuals were arrested in connection with the conspiracy. Among them, it was revealed that Savarkar, along with his two brothers, played a central role as the mastermind, leader, and driving force behind the conspiracy.
- During the trial, Savarkar was identified as the principal figure responsible for the long-standing conspiracy and was sentenced to life imprisonment and the forfeiture of all his property.
| The Rand Murder at Poona, 1897
The Rand Murder at Poona in 1897 was a significant event in the context of the Indian nationalist movement during the British colonial period. The murder was committed by the Chapekar brothers, Damodar and Balkrishna, who were Chitpavan Brahmins, against Mr Rand, the President of the Plague Committee in Poona. The assassination was a response to the Plague Committee’s policies, which were perceived as oppressive and tyrannical.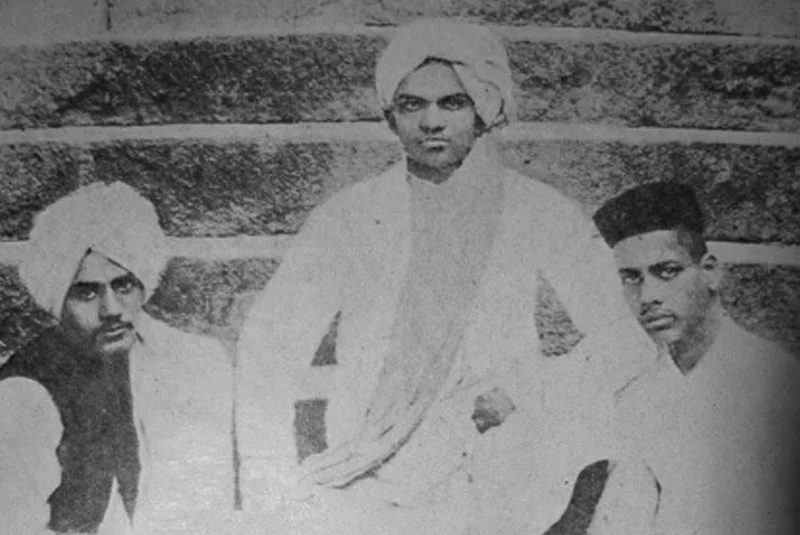  Bal Gangadhar Tilak, a prominent nationalist leader and journalist, was associated with this incident due to his writings in his newspaper, Kesari. In his newspaper, Tilak made statements that were seen by some as justifying the use of violence against the British colonial authorities. For example, he referenced the Bhagavad Gita and its teachings on duty and action. However, Tilak’s intent may not have been to explicitly incite violence but rather to emphasize the importance of selfless and principled action. Tilak was prosecuted for seditious writings against the British Government, and he received an 18-month sentence of rigorous imprisonment as a result. The authorities considered his writings to have influenced the Chapekar brothers in their violent acts. |
Revolutionary Activities in Punjab
The revolutionary activities in Punjab during the British colonial period were marked by courageous individuals and groups who fought tirelessly for independence. Revolutionary nationalism in Punjab was fueled by several issues, including frequent famines, rising land revenue and irrigation taxes, and the practice of ‘begar’ by zamindars (forced labour without pay).
| YEAR | PERSONALITY | PLACE | WORK |
| 1906 | Rash Behari Bose and Sachin Sanyal | Punjab, Delhi, and the United Province | Organized a secret society in Punjab, Delhi, and the United Provinces, while individuals like Hemachandra Kanungo sought military and political training abroad. |
| 1912 | Rash Behari Bose, Sachin Sanyal, Basant Kumar Biswas, Amir Chand and Avadh Behari | Delhi | Staged a bomb attack on Viceroy Hardinge, in Chandni Chowk, Delhi. All were convicted but Rash Behari Bose, the person behind the plan, managed to escape. |
Major Revolutionary Activities
- Lala Lajpat Rai, who published the “Punjabee” with its motto of self-help at any cost, and Ajit Singh, who was Bhagat Singh’s uncle.
- Formation of Anjuman-i-Mohisban-i-Watan: Ajit Singh organized the extremist Anjuman-i-Mohisban-i-Watan in Lahore, along with its journal “Bharat Mata.” Before Ajit Singh’s group embraced extremism, it focused on advocating non-payment of revenue and water rates among Chenab colonists and Bari Doab peasants.
- Other leaders in this movement included Aga Haidar, Syed Haider Raza, Bhai Parmanand, and the radical Urdu poet Lalchand ‘Falak.’
Government Repression And Its Impact On Revolutionary
Decline of Extremism: Extremism in Punjab experienced a decline after the government took action in May 1907 by banning political meetings and deporting Lajpat Rai and Ajit Singh.
- Following this, Ajit Singh and a few of his associates, including Sufi Amba Prasad, Lalchand, Bhai Parmanand, and Lala Hardayal, evolved into full-fledged revolutionaries.
- During the First World War, Rash Behari Bose emerged as a leading figure in the Ghadar Revolution. Towards the end of 1913, Bose met with Jatin to explore the possibilities of a nationwide armed uprising similar to the 1857 revolt.
- He collaborated with Bagha Jatin, extending the Bengal plan to Punjab and the upper provinces.
- However, the revolution plan did not succeed, leading Rash Behari Bose to escape to Japan in 1915. Much later, he played a significant role in the founding of the Indian National Army.
| VIEWS |
| Subhash Chandra Bose
“The ultimate object of the revolutionaries is not terrorism but revolution and the purpose of the revolution is to install a national government.” |
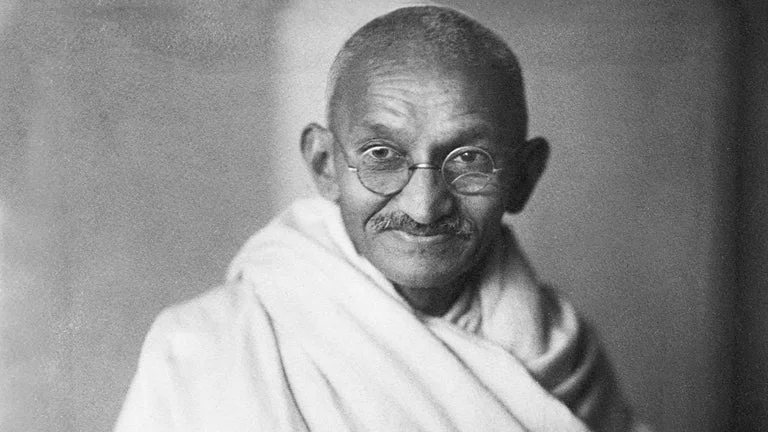
| M.K Gandhi
“Will you not see the writing that these terrorists are writing with their blood?” |
| Madanlal Dhingra
“Neither rich nor able, a poor son like myself can offer nothing but his blood on the altar of mother’s deliverance… may I be reborn of the same mother, and may I die in the same sacred cause, till my mission is done and she stands free for the good of humanity and the glory of God.” |
| B.G. Tilak in Kesari (June 15, 1897)
“God has not conferred upon the foreigners the grant inscribed on a copper plate of the kingdom of Hindustan… Do not circumscribe your vision like a frog in a well; get out of the Penal Code and enter the extremely high atmosphere of the Srimad Bhagavad Gita and consider the actions of great men.” |
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
The key role in the fight for independence in India was played by the revolutionary movements in Maharashtra and Punjab. In Maharashtra, individuals such as Phadke, Tilak, and Savarkar spearheaded armed rebellions and militant patriotism, enduring harsh crackdowns yet playing important roles in the fight for independence. In Punjab, figures like Rash Behari Bose and Lala Lajpat Rai incited revolutionary passion by forming secret groups and carrying out bomb strikes. Despite severe government repression, their actions set an essential groundwork for India’s future freedom.
| Related Articles | |
| Lala Lajpat Rai Jayanti 2024 | Revolutionary Activities in India: Struggle Against Colonial Oppression |
| Economic Impact Of British Rule In India | The Revolt of 1857 |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program














