Introduction: Captivating Solar Eclipses
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, temporarily blocking out the Sun’s light. This celestial event creates a mesmerizing spectacle as day turns into an early twilight. There are two main types of solar eclipses: total and partial.
Solar eclipses captivate observers worldwide, offering a unique and awe-inspiring display of our solar system’s cosmic dance.
Solar Eclipse: Celestial Alignments and Shadowy Phenomena
Eclipses are intriguing astronomical events that transpire when one celestial body ventures into the shadow of another.
- This captivating phenomenon unfolds when three celestial objects align in a straight line, a configuration referred to as “syzygy.”
- Two Types of Earthly Eclipses: The Earth experiences two primary types of eclipses due to the unique orbital planes of its moon and its orbit around the Sun.
- These celestial alignments result in solar and lunar eclipses, each with its own distinct characteristics and visual spectacle.
Solar Eclipse: Causes and Shadows
A solar eclipse, known as “Surya Grahan” in some cultures, is a remarkable astronomical event marked by the Moon positioning itself between Earth and the Sun.
- During this event, the Moon’s interposition obscures the Sun, momentarily casting a shadow over a portion of the Earth, either completely or partially.
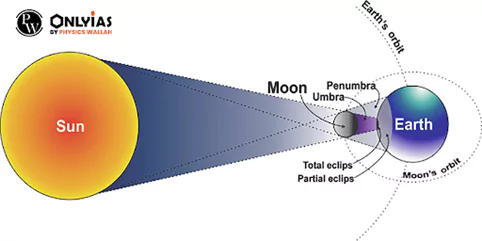 How Solar Eclipses (Surya Grahan) Occur : The occurrence of a solar eclipse hinges on a precise alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth.
How Solar Eclipses (Surya Grahan) Occur : The occurrence of a solar eclipse hinges on a precise alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth.
- It is when the Moon passes directly between Earth and the Sun that the Sun’s radiant light is momentarily concealed from view.
- Moon’s Orbital Influence : Solar eclipses take place approximately every six months during the new moon phase.
- This timing coincides with when the Moon’s orbital plane is in close proximity to the plane of Earth’s orbit.
- This synchronized celestial dance creates the conditions necessary for this captivating spectacle to unfold.
- Shadow Formation During Solar Eclipses : During a solar eclipse (Surya Grahan), two distinctive shadows are cast upon the Earth by the Moon, each offering a unique viewing experience:
- The Umbra: It represents the innermost and darkest region of the Moon’s shadow.
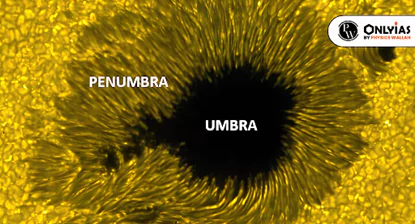 Those situated within the umbra are in for a spectacular treat – a total eclipse.
Those situated within the umbra are in for a spectacular treat – a total eclipse. - As this shadow extends towards Earth, it gradually shrinks in size, creating a path of complete darkness.
- The Penumbra: The Penumbra, in contrast, is the outer part of the Moon’s shadow.
- It encompasses a larger area as it stretches towards Earth.
- Within the penumbra, observers are treated to a partial eclipse, where the Sun is only partially obscured.
- This broader region provides a unique celestial display, distinct from the totality of the umbra.
- The Umbra: It represents the innermost and darkest region of the Moon’s shadow.
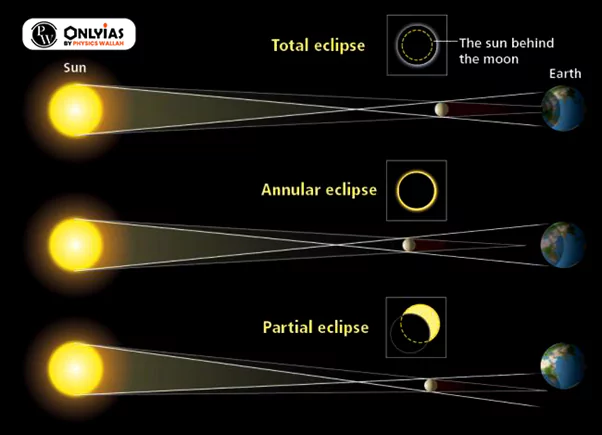
Phases of a Solar Eclipse (Surya Grahan): From Annular to Total and Beyond
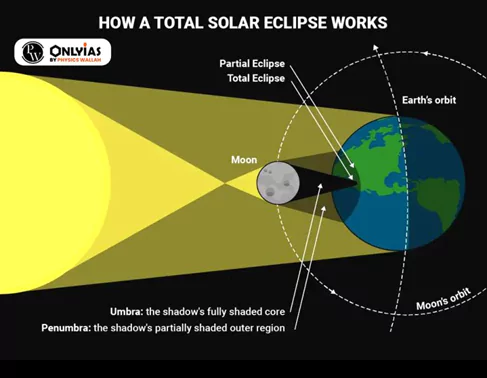
From Annular to Total and More
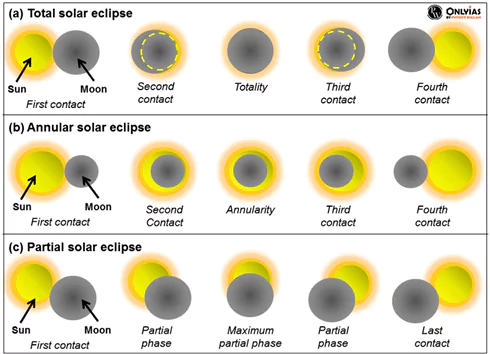
- Annular Solar Eclipse: Annular solar eclipse or Ring of Fire takes place when the Moon comes between the Sun and Earth while it is at its farthest point from Earth.
- The Moon looks smaller than the Sun as it is at its farthest point and hence does not cover the Sun completely.
- Total Solar Eclipse (Surya Grahan): This phenomenon occurs when the Moon completely blocks out the Sun.
- As a result, the sky will darken completely.
- Hybrid Solar Eclipse: It is a combination of total and annular eclipse.
- At some points on Earth, it appears as a total eclipse, whereas at other points it appears as annular.
- Partial Solar Eclipse: This phenomenon occurs when the Sun and Moon are not exactly in line with the Earth, and the Moon only partially covers the Sun.
- However, partial eclipses are hardly noticeable as it requires 90% coverage of the Sun to notice any darkening.
The Scientific Impact of Solar Eclipses (Surya Grahan) on Earth and Beyond
- Study Temperature Variation: Temperature drop during an eclipse can lead to cooling of the upper atmosphere.
- This event is likely to affect the temperature structure of the ionosphere.
- Radio Frequency Variation: Electron density in the ionosphere will decrease due to cooling in the ionosphere.
- This will have an impact on propagation of radio waves, particularly of high frequency.
- Satellite Communication Challenges: Anomalies in the ionosphere will impact satellite-based navigation signals and also communication.
- Studying Environmental Changes: Studies have shown that solar eclipses (Surya Grahan) can alter Earth’s temperature, relative humidity, wind speed and also ozone density.
- Helps in Solar Studies: Eclipses of the Sun allow scientists to study the Sun’s atmosphere called the corona, which otherwise is not possible due to the bright light of the Sun.
How Solar Eclipses (Surya Grahan) Shaped Celestial Understanding
- Contributions to Understanding Celestial Mechanics
- Chinese: The Chinese constructed sophisticated observatory buildings for viewing solar eclipses (Surya Grahan).
- There were astrologers to predict the Emperor’s future using observations.
- Greek Culture: Greek astronomers made observations during eclipses and proposed the first known heliocentric model of the Universe.
- Chinese: The Chinese constructed sophisticated observatory buildings for viewing solar eclipses (Surya Grahan).
Solar Eclipses (Surya Grahan) Across Cultures: Spiritual, Artistic, and Historical Significance
- Indian Culture:
- Evidence: The oldest reference of Eclipse in India is in the Rig Veda that describes the effect of eclipse.
- Means of Attaining Salvation: Skanda Purana has a legend where sages witness a forest-dwelling woman transform into a beauty after bathing in a holy lake during a solar eclipse (Surya Grahan), implying that it is a way of attaining salvation.
- Ancestral Duties: According to Padma Purana, a man who offers water to his ancestors during a solar eclipse (Surya Grahan) achieves heaven.
- However, he becomes a Chandala in case of failure to do so.
- Influence on Art, Literature, and Religion
- Art: Eclipse has been portrayed in paintings as a monster, dragon, and even a celestial dog, swallowing the sun in ancient Maya and Chinese culture.
- They were used in the backdrop of European Renaissance crucifixion scenes to give a sorrowful effect.
- Literature: In Homer’s Odyssey, the protagonist returns to his kingdom, accompanied by a seer’s vision of an eclipse.
- Art: Eclipse has been portrayed in paintings as a monster, dragon, and even a celestial dog, swallowing the sun in ancient Maya and Chinese culture.
- Egyptian Culture: In ancient Egypt, the King who saw himself as a representative of the Sun went around the city to reassure people.
- Chinese Culture: Chinese considered eclipses to be omens that predicted the future of the Emperor, and hence was important to predict eclipses.
| Previous Year Questions
Q.1) In the northern hemisphere, the longest day of the year normally occurs in the: (2021)
Ans: b Q.2) On 21st June, the Sun (2019)
Ans: a |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program










