The Speaker of the Lok Sabha plays a crucial role in India’s parliamentary system. Elected by the members, the Speaker maintains order and ensures smooth proceedings in the House. With significant powers and responsibilities, the Speaker upholds impartiality and democratic values. This article explores the provisions and functions of the Speaker, highlighting their importance in the legislative process.
The Speaker of Lok Sabha
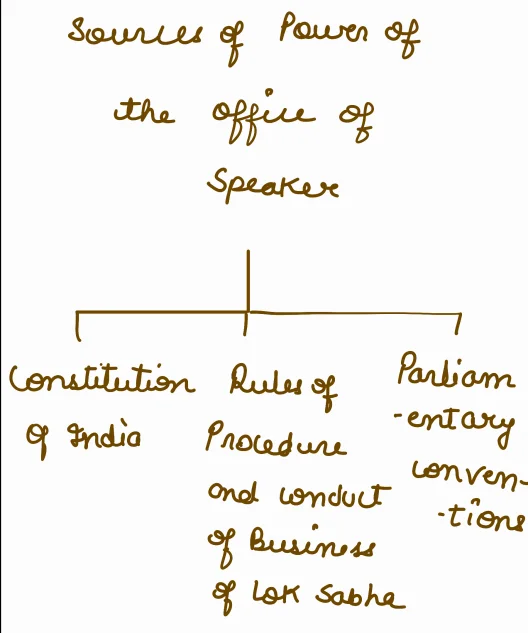
Provisions Related to the Speaker of Lok Sabha
- Constitutional Provisions (Articles 93 to 97): Article 93 to 97 of the Indian Constitution constitute provisions related to both Speaker and Deputy Speaker.
- Article 93 of the Constitution provides for the Speaker and Deputy Speaker positions for the Lok Sabha.
- Election Process: The Speaker is elected by the members of Lok Sabha from amongst themselves by a simple majority of the members present and voting in the House.
- Powers and Authority: He enjoys vast authority and powers, under the Constitution and the Rules, as well as conventionally.
- The President fixes the date of election of the Speaker.
- Tenure During Dissolution: Whenever the House of the People is dissolved, the Speaker shall not vacate his office until immediately before the first meeting of the House of the People after the dissolution.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Powers and duties of the office of the Speaker in India –
| Categorisation of Powers | Power/Duty | Further Description |
| Conduct of Proceedings | Maintaining Order and Decorum in the House |
|
| Interpretative Authority | Final Interpreter of Constitutional and Legislative Provisions in the House |
|
| Regulatory Functions | Adjournment in Absence of Quorum |
|
| Voting Powers | Casting Vote in Case of a Tie |
|
| Joint Session Leadership | Presiding Over Joint Sessions of Parliament |
|
| Confidential Proceedings | Permission for ‘Secret’ Sittings |
|
| Legislative Powers | Deciding on Money Bills |
|
| Member Disqualification | Disqualification on the Grounds of Defection |
|
| Parliamentary Liaison | Ex-Officio Chairman of Parliamentary Groups and Conferences |
|
| Committee Oversight | Appointments to Parliamentary Committees |
|
Provisions Related To The Independence Of Office Of The Speaker
- Impartiality and Equal Treatment: The Speaker is a respected and powerful figure who must act impartially, treating all Parliamentary members equally regardless of their party affiliation.
- Ensuring Democratic Proceedings: This ensures democratic proceedings, giving each member the opportunity to be heard.
- The impartiality of the office is ensured by the following provisions.
| Provision for Independence and Impartiality | Description |
| Security of Tenure |
|
| Financial Independence |
|
| Protection from Discussion and Criticism |
|
| Judicial Immunity |
|
| Casting Voting Rights |
|
| High Rank in Order of Precedence |
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
In summary, the Speaker of the Lok Sabha is vital for effective governance and parliamentary democracy.
- Their authority extends to maintaining decorum, interpreting rules, and overseeing legislative processes.
- The provisions ensuring their independence further strengthen their role. Understanding these aspects helps appreciate the Speaker’s influence on India’s legislative framework.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| 2024 Lok Sabha Election Results Live Updates | Money Bill (Article 110) |
| Constitution: A Living Document | The Importance Of Being The Lok Sabha Speaker |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









