The Parliament of India, the supreme legislative body of the Union Government, is central to the country’s democratic framework. Encompassing the President, the Rajya Sabha (Council of States), and the Lok Sabha (House of the People), it operates under Articles 79 to 122 of the Constitution. These provisions define its composition and functions, emphasizing its role in shaping and sustaining India’s democracy.
Structure and Composition of Parliament in India: An In-Depth Overview
Introduction to the Temple of Democracy
- The Parliament, the supreme legislative organ of the Union Government of India, plays a pivotal role in shaping the democratic ethos of the nation.
- Intricately designed, its composition and functions are enshrined within the Constitution, illuminating the essence of democracy.
- Constitutional Provisions: Encompassed within Part V of the Constitution, Articles 79 to 122 lay down the detailed provisions pertaining to the Parliament.
- Composition of the Parliament: Specifically, Article 79 stipulates the Parliament’s composition, which is an amalgamation of three critical elements: the President, the Council of States (Rajya Sabha), and the House of the People (Lok Sabha).

Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Structure of the Indian Parliament
Comprises three parts ( as per Article 79 of the Indian Constitution )
- In 1954, the Council of States and the House of the People adopted Hindi names: ‘Rajya Sabha’ and ‘Lok Sabha and the President.
- The change symbolized India’s cultural pride post-independence.
- It reflects the nation’s democratic will.
Role of the President vis-a-vis Parliament
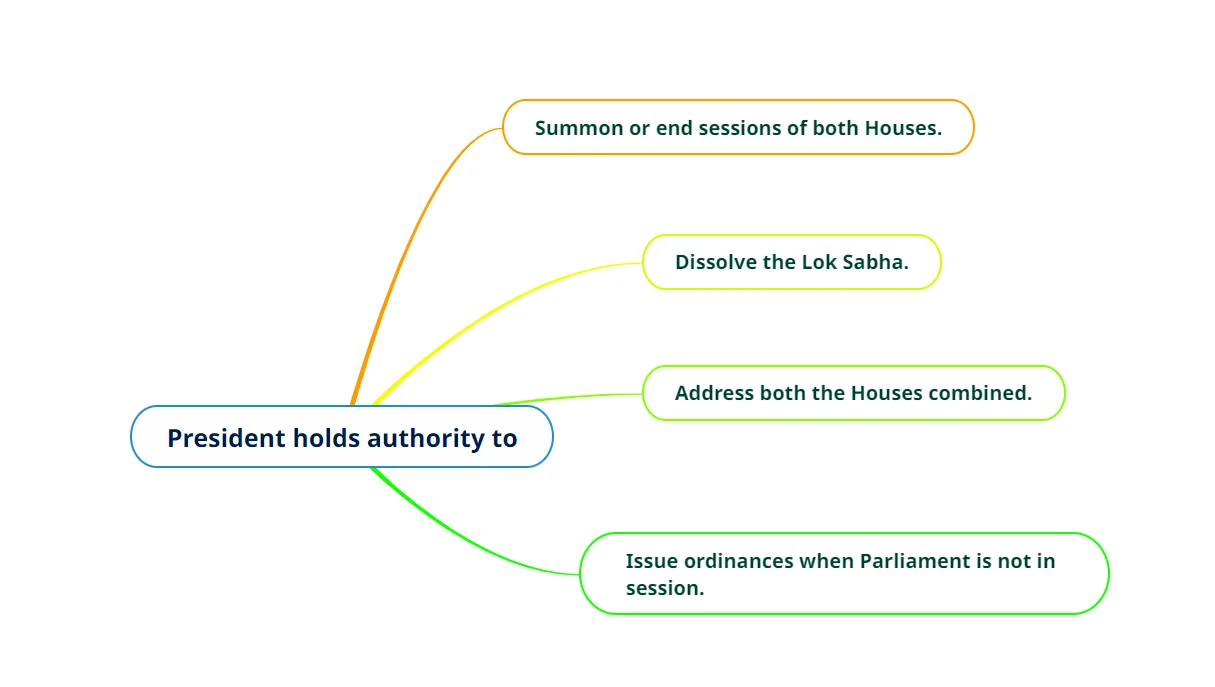
- Constitutional Duties: The President’s constitutional duties in relation to Parliament include summoning (Article 85), proroguing, dissolving Parliament, and delivering an annual address to both Houses.
- Symbolic and Practical Significance: The President holds both symbolic and tangible importance in the legislative process. No bill can become law without the President’s approval.
- Communication and Recommendations: The President, though not a member of either House, communicates messages, recommends certain Bills, and has the power to issue Ordinances when Parliament is not in session (Article 123 – Power to issue ordinances).
- Disqualification Matters: The President also decides on disqualification matters of Member of Parliament, guided by the advice of the Election Commission (Article 103)
The Rajya Sabha: A Federal Character with Unique Representation ( Article 80 )
- Structure and Composition of Legislative Assemblies: The structure and composition of any country’s legislative assembly reflect its inherent democratic principles and values.
- Role of the Rajya Sabha: The Rajya Sabha often referred to as the ‘Council of States‘, plays a pivotal role in representing both the territorial regions and expertise from various fields.
Strength
- Cap on Rajya Sabha Membership: The Rajya Sabha’s strength is constitutionally capped at 250 members article 80(1).
- Composition of Rajya Sabha: Most of this number, precisely 238, are representatives of the states and union territories.
- Indirect Election Process: These members are not directly elected by the general populace; instead, they are chosen indirectly through a designated electoral process.
- Presidential Nominations: Additionally, 12 members of this assembly are nominated by the President of India.
- Current Strength of the Rajya Sabha: The present strength of Rajya Sabha, however, is 245, out of which 233 are representatives of the States and Union territories of Delhi, Puducherry and Jammu and Kashmir (w.e.f. 31.10.2019) and 12 are nominated by the President.

Importance of Allocation in Representation Dynamics
This allocation is pivotal in understanding the representation dynamics:
- State Representation in Rajya Sabha:
-
-
- Elected by the elected members of the state legislative assemblies in accordance with the system of proportional representation by single transferable vote, seat allocation is based on the population size of the state.
- Uttar Pradesh has 31 seats; Tripura has 1.
- India vs. USA: In the USA, all states have equal Senate representation (2 per state, Total 100 members).
-
- Union Territories’ Representation:
-
- Selection of Union Territory Representatives: The representatives of the Union territories in the Council of States are chosen in such a manner as Parliament may, by law, prescribe.
- Legal Framework for Filling Seats: Part IVA of the Representation of the People Act, 1950, provides for the manner of filling seats in the Rajya Sabha allocated to Union territories.
- Electoral College for Union Territories: Section 27A of that Act provides that for the purpose of filling any seat or seats in the Council of States allotted to any Union territory in the Fourth Schedule to the Constitution, there shall be an electoral college for each such territory.

- Nominated Members:
-
- Unlike the USA’s Senate, the Rajya Sabha has nominated members.
- Criteria for Nomination: Article 80(3) provides that 12 members nominated by the President shall consist of persons having special knowledge or practical experience in respect of such matters as literature, science, art and social service.
The Lok Sabha: A Deep Dive into the Composition of India’s House of the People ( Article 81 )
- Article 79: House of the People: As per the provision of Article 79 of Indian constitution, the House of the people, the Lok Sabha is the lower House of the Parliament.
- Composition of the Lok Sabha: Lok Sabha is composed of representatives of the people chosen by direct election on the basis of the adult suffrage.
- Maximum Strength of the Lok Sabha: The maximum strength of the house envisaged by the Constitution is 552 ( now 550 after termination of reserved seat of anglo-indians by 104th Constitutional Amendment Act, passed in January 2020 , also extended the reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) in the Lok Sabha and State Assemblies for another ten years, until January 25, 2030.).
- Distribution of Seats: Out of 550 this, 530 members are to be the representatives of the states and 20 members are to be the representatives of the union territories.
- Current Membership of the Lok Sabha: At present, the Lok Sabha has 543 members. Of these, 524 members represent the states and 19 members represent the union territories.
Delving Into The Specifics Of This Composition
- State Representation in Lok Sabha:
- Citizens from constituencies of all states aged 18+ have universal adult franchise to elect representatives from territorial constituencies within states directly.
- 61st Constitutional Amendment Act, 1988 reduced the voting age from 21 to 18.
- Union Territories’ Representation:
- Parliament outlined selection procedures for union territories‘ Lok Sabha representatives via the Union Territories (Direct Election to the House of the People) Act in 1965, ensuring their direct election.
- Nominated Members:
- Nomination of Anglo-Indian Members: Before 2020, the President nominated two members from the Anglo-Indian community to the Lok Sabha, if the community was not adequately represented.
- Original Duration of the Provision: Originally, this provision was to operate for ten years (ie., upto 1960) only.
- Later, this duration has been extended continuously since then by ten years each time.
- The last extension upto 2020 was made by the 95th Amendment Act, 2009.
- Discontinuation of the Provision: But, the 104th Amendment Act, 2019, has not further extended the operation of this provision.
- In other words, the Amendment discontinued this provision of special representation of the Anglo-Indian community in the Lok Sabha by nomination.
- Consequently, this provision ceased to have effect on the 25th January, 2020.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
The Parliament of India, through its structured composition and defined roles, embodies the nation’s democratic values and federal principles.
- By representing diverse interests through the Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha, it ensures a balanced legislative process.
- This institution remains pivotal in fostering democracy, maintaining federal balance, and addressing the aspirations of India’s diverse populace.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Features of Indian Constitution | Election Commission of India |
| Rajya Sabha Election 2024 | Indian Parliament |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









