A constitution is a fundamental set of principles that outlines how a government should operate and the relationship between the state and its citizens. It establishes the structure of government and ensures that laws are applied equally to everyone.
- Rule of Law: This means no one, including the government, is above the law.
- Constitutionalism: It ensures that government powers are limited and accountable.
Meaning of Constitution
Origin: Constitution derives from the Latin constituere, which means to establish or ‘to set up’.
- Contemporary Meaning of ‘Constitution’: Constitution denotes a collection of principles that delineate the structure and functioning of the government, as well as the dynamic interplay between the government and the populace concerning their respective rights and responsibilities.
- The ‘Rule of Law‘: Constitutions are the bedrock of any nation’s governance system, providing a framework of laws and principles that guide the functioning of the state. This framework of laws is more popularly known as the ‘Rule Of Law.’
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Concept of Rule of Law
Historical Background: The principle of ‘Rule of Law’ is centuries old. Its current form is defined by A.V. Dicey, the British jurist.

- Definition of the ‘Rule of Law’: It states that the law has absolute supremacy and no individual or institution, including the government, is above the Law.
- The government must act within the bounds of the Law.
- This means that no one is punished except for a clear violation of the law.
- Application in India: While the first and second elements find application in the Indian legal system, the third element does not.
- In India, individual rights are derived from the Constitution itself.
- Constitutional Significance: The Supreme Court, recognizing the significance of the ‘Rule of Law,‘ has declared it as a ‘Basic Structure’ of the Constitution.
- Consequently, this fundamental principle cannot be dismantled, even through Constitutional amendments.
Constitutionalism
According to Friedrich: “Constitutionalism provides a system of effective restraints upon governmental action. It is a body of rules ensuring fair play, thus rendering the government responsible”.
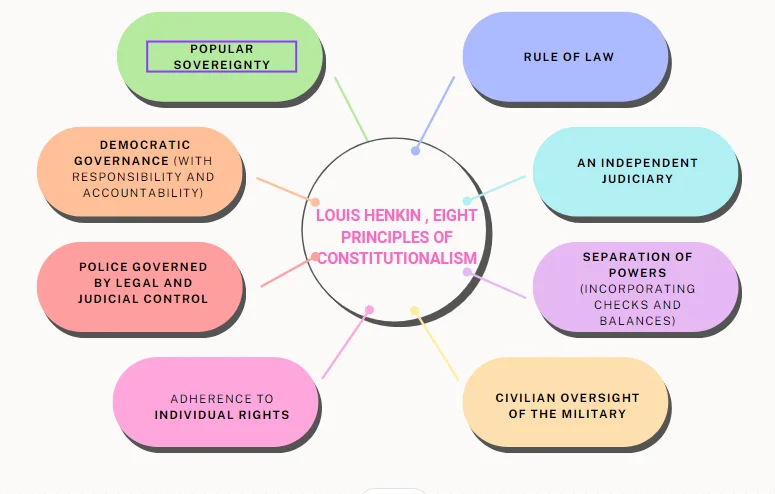
The concepts of Constitution and Constitutionalism share a close relationship, yet they exhibit distinct differences:
- Presence of ‘Constitutionalism’: While a country may possess a ‘Constitution,’ the presence of ‘Constitutionalism’ is not guaranteed.
- ‘Constitutionalism’ vs. Dictatorship: For instance, in a dictatorship where the ruler’s decrees hold absolute authority, there exists a ‘Constitution’ but lacks ‘Constitutionalism.’
- Limiting Government Authority: Constitutionalism acknowledges the necessity of a government with authority but insists on placing limitations on that authority.
- Unrestricted power can lead to an authoritarian and oppressive government, posing a threat to the freedom of the populace.
- A country embodies not just a ‘Constitution’ but also ‘Constitutionalism’ when its Constitution imposes constraints on governmental power.
- Role of Constitution in ‘Constitutionalism’: Constitutionalism envisions a polity governed by a Constitution that fundamentally advocates limited government and the rule of law, contrasting with arbitrary, despotic, authoritarian, or totalitarian rule.
- Alignment with Democratic Principles: For Constitutional government to be meaningful, it must inherently align with democratic principles.
- Any form of arbitrary power, even if sanctioned by a Constitutional document, contradicts the essence of Constitutionalism.
- Justification for a Limited Government: The essence of Constitutionalism lies in aspiring to establish a political order where governmental powers are restricted, essentially advocating for a limited and, therefore, “civilised” government.
- The true justification for a Constitution lies in fostering a “limited government” and compelling those in governance to adhere to established laws and regulations.
Types Of Constitution
Constitutions, which serve as the fundamental laws outlining the principles by which a state is governed, can be classified into various types based on their formation, flexibility, and the nature of their rules and regulations. The primary types of constitutions are:
| Serial No. | Types of Constitutions: Description | |
| 1 |
|
|
| 2 |
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
| 4 |
|
|
| 5 |
|
|
| 6 |
|
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
Constitutions come in various forms, such as written or unwritten, flexible or rigid, and federal or unitary. They can also be presidential or parliamentary, monarchical or republican, and theocratic or secular. Understanding these types helps in grasping how different governments function and ensure that power is exercised fairly and responsibly.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Constitution: A Living Document | Supreme Court |
| Fundamental Rights (Article 12-35) | Rule of Law in Democracy |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









