Parliamentary privileges are special rights and immunities granted to the Parliament, their committees, and their members. These privileges are crucial for maintaining the independence and effectiveness of parliamentary actions. They ensure that members can fulfil their responsibilities without external interference. However, the President, despite being part of Parliament, is not covered by these privileges.
Parliamentary Privileges: Significance, Categories, and Issues
Definition and Scope of Parliamentary Privileges
- Meaning: Parliamentary privileges encompass special rights, immunities, and exemptions granted to the two Houses of Parliament, their committees, and their members.
- Purpose of Parliamentary Privileges: These privileges are essential to ensure the independence and effectiveness of their actions.
- Importance of Privileges: Devoid of these privileges, the Houses would struggle to maintain their authority, dignity, and honour, and their members would be vulnerable to obstructions in fulfilling their Parliamentary responsibilities.
- Extension of Privileges: Notably, the Constitution extends these privileges to individuals entitled to speak and participate in the proceedings of a House or its committees, including the Attorney General of India and Union ministers.
- Exclusion of the President: It is important to clarify that these privileges do not apply to the President, who, despite being an integral part of Parliament, is not covered by Parliamentary privileges.

Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Significance of Parliamentary Privileges
- Safeguarding Freedom of Speech and Expression: The importance of Parliamentary privileges lies in safeguarding the freedom of speech and expression for Members of Parliament,
- Preserving the authority and dignity of the Parliament, and
- Shielding its proceedings from external interference, including the courts of law.
- Effective Exercise of Constitutional Functions: These privileges serve the purpose of facilitating the effective exercise of constitutional functions by Parliamentarians and regulating the behavior of members.
Categories of Parliamentary Privileges
- Parliamentary privileges can be categorized into two groups:
- Collective privileges of the Houses
- Individual privileges of members.
Collective Privileges of the Houses
The collective privileges of each House of Parliament encompass:
- Entitlement to Publish Reports: The Parliament’s entitlement to publish reports, debates, and proceedings.
- Authority to Exclude Strangers: The authority to exclude strangers from its proceedings and to hold secret sittings.
- Right to Information on Members’ Legal Status: The right to receive information regarding the arrest, detention, conviction, or release of its members.
- Rule Establishment and Adjudication: The capacity to establish rules governing the conduct of its proceedings and to adjudicate on such matters.
- Rule Establishment and Adjudication: The ability to impose sanctions on both members and non-members for violating these privileges by reprimand, admonition or imprisonment (suspension or expulsion in case of members).
- Legal Immunity within House Premises: No legal proceedings can be initiated against any person within the House premises without the presiding officer’s permission.
- Prohibition on Court Investigations: Courts are prohibited from investigating the proceedings of the House or its committees.
- Power to Conduct Inquiries: It can conduct inquiries and order the attendance of witnesses and send for relevant papers and records.
Individual Privileges of Members
Members enjoy specific privileges individually, including:
- Protection from Arrest: Members are protected from arrest during the session and 40 days before and after Parliament’s session.
- It’s important to note that this protection is applicable only in civil cases and does not extend to criminal or preventive detention cases.
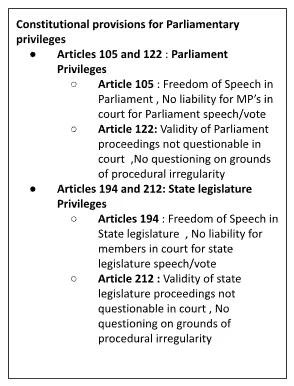
- Freedom of Speech and Expression: Members of Parliament have the freedom of speech and expression.
- While the freedom of speech and expression for other citizens under Article 19(1)(a) is subject to certain restrictions (as per Article 19(2), members face no such limitations for their expressions within the Parliament.
- However, this freedom is subject to the rules of procedure of the Houses (Article 118).
- Freedom as Witness: Members cannot be summoned to give evidence as a witness during Parliament’s session without the leave of the House.
- Authority to Impose Penalties: It’s noteworthy that Parliament has the authority to impose penalties on both its members and outsiders for violating these privileges.
Breach of Privileges and Contempt of House
Breach of Privileges: Breach of privileges occurs when the rights , privileges or immunities, of either the Members individually or of the House in its collectively, are disregarded or attacked.
- Contempt of the House: Any act which obstructs the functioning, threatens the dignity or disregards the authority of the House, its members or its officers is treated as a contempt of the House.
- A few examples of breach of privileges and contempt of the House are:
- The threat of violence against a member of the House.
- Publication of a false report of the proceedings of the House.
- Speeches or publications that reflect on the House, its members or its Committees.
- A few examples of breach of privileges and contempt of the House are:
- Relationship Between Breach of Privileges and Contempt of the House: A Breach of privilege may amount to contempt of the House.
- Contempt of the House Including Breach of Privilege: Similarly, a contempt of the House may include a breach of privilege but there could be a Contempt of the House without breaching a privilege.
- Contempt Without Breach of Privilege: One such example is when a person disobeys a legitimate order of the House; it is a contempt of the House but no breach of privilege is committed.
Issues Regarding Parliamentary Privileges
Status of Parliamentary Privileges: The Constitution stipulated that until Parliament enacts a law to formalize these privileges, the Houses and their members would continue to enjoy the privileges held by the House of Commons before the Constitution came into effect.
- 44th Amendment and Parliamentary Privileges: In 1978, the 44th Amendment brought about a superficial change in Article 105, removing the reference to the House of Commons from the Indian Constitution.
- However, the essential stance on privileges remained unchanged.
- Lack of Codification: To date, Parliament has not passed any legislation to codify these privileges, leading to numerous instances where conflicts have arisen between the fundamental rights of individuals to express their views on Parliamentary proceedings and the privileges of the Houses.
- Instances have occurred where Houses of Parliament or State legislatures have ordered the arrest of individuals for breaching privileges.
- Keshav Singh Case: The Supreme Court responding to a Presidential reference under Article 143, asserted that in situations where there is a conflict between privileges and provisions related to fundamental rights, efforts should be made to reconcile the conflict through harmonious construction.
- Recommendations Against Codification: In 2008, the Lok Sabha Committee of Privileges recommended against codifying Parliamentary privileges, stating it was unnecessary.
- However, the lack of political will to formalize these privileges has caused conflicts between citizens’ fundamental rights and legislative privileges.
- Enacting legislation to codify these privileges could resolve these issues effectively.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
Parliamentary privileges safeguard the authority and dignity of Parliament, enabling members to perform their duties freely.
- Yet, the lack of codification has led to conflicts with fundamental rights.
- Addressing this through legislation can balance citizens’ rights with parliamentary privileges, enhancing democratic governance.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Parliamentary Privileges: Rights, Breaches, and Implications | Houses of Parliament |
| Attorney General of India | Constitution: A Living Document |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









