The Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG), established under Article 148 of the Indian Constitution, is a constitutional body appointed by the President. CAG plays a crucial role in ensuring accountability by independently auditing government finances, identifying financial irregularities, and issuing audit reports. This institution is essential for overseeing public funds effectively, thereby maintaining transparency and financial integrity within the government.
The Role and Importance of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India
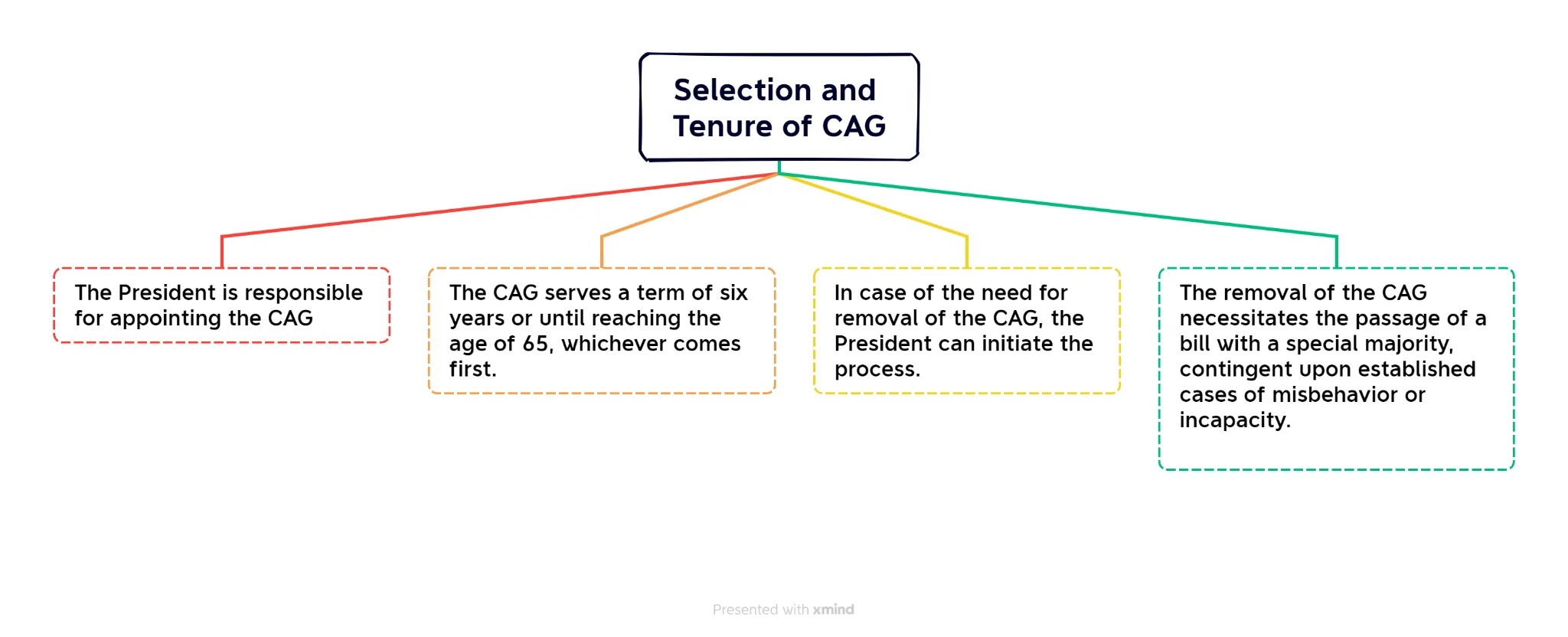
Appointment and Service Conditions of CAG as per Article 148 are as follows
- Appointment and Removal: The Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) is appointed by the President of India and can be removed from office only in the manner and on the grounds of a Judge of the Supreme Court.
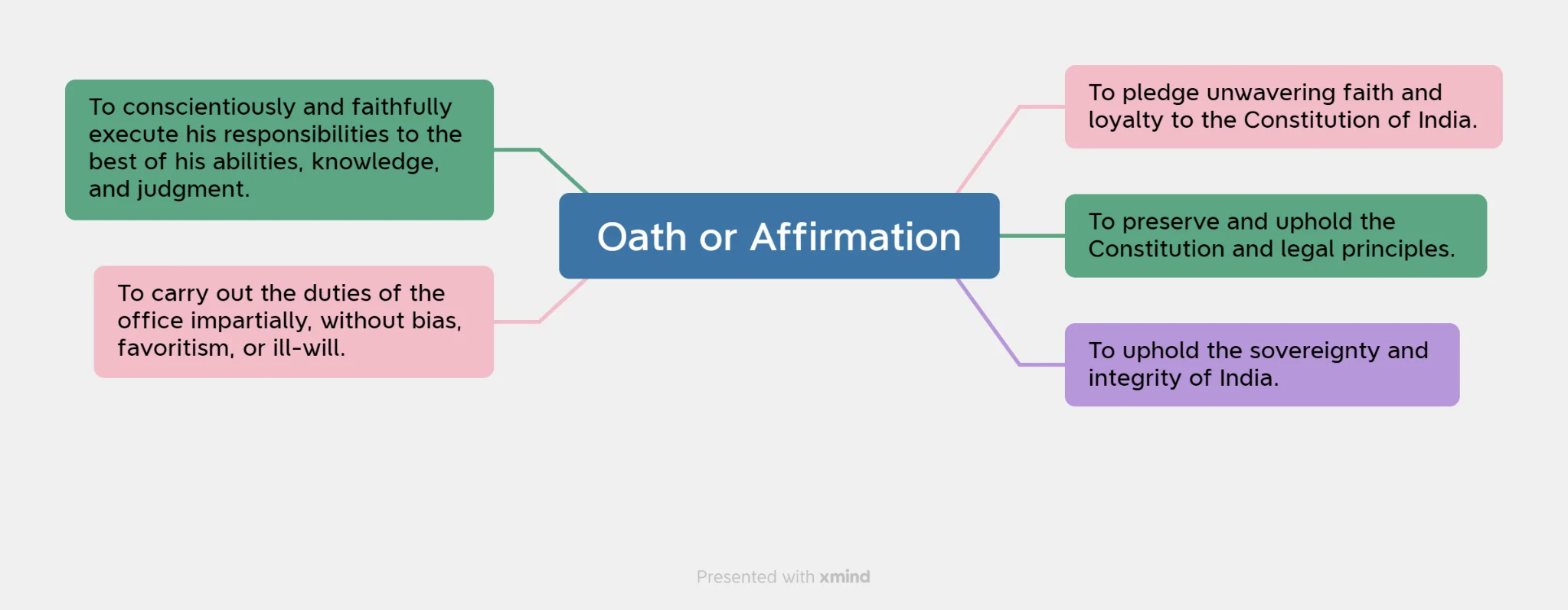
- Oath: The person appointed to this office should take an oath of office before the President or any other person appointed by the office of the President.
- Service Conditions: The salary, service conditions, leaves of absence, pension, and age of retirement are determined by the Parliament of India by law until they are so determined, shall be as specified in the Second Schedule such that the service conditions and salary will not be modified to the disadvantage of the incumbent during their tenure.
- Re-appointment: The CAG is not eligible for any further office either in the Government of India or any State Government after the end of their tenure.
- Power of Parliament: The conditions of service for individuals serving in the Indian Audit and Accounts Department are subject to the provisions of the Constitution and any law made by Parliament.
- The administrative powers of the Comptroller and Auditor-General shall be determined by rules prescribed by the President.
- The President must consult with the Comptroller and Auditor-General when making these rules.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Functions of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG)
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar said, “the CAG will be the most significant officer under the Indian Constitution.”
CAG derives its audit mandate from different sources like –
|
- Audit of Accounts Related to Expenditure
-
- Consolidated Fund of India
- Consolidated Fund of each State and Union Territory having a Legislative Assembly.
- Contingency Fund of India
- Public Account of India
- Contingency Fund and Public Account of each State
- Audit of stocks and stores as well as government inventory.
- Ensure that no pilferages have taken place from it.
- Ensuring Compliance with Rules and Procedures
- Effective Check on Assessment, Collection, and Proper allocation of revenue.
- Audit of Bodies and Authorities Substantially Financed from Central or State Revenues
- Government Companies and Other Corporations and Bodies as Required by related Laws.
- Assists the Public Accounts Committee in Financial Matters
- Vital Role in Ensuring Accountability and Transparency in Financial Matters
- Advise the President on prescribing the form in which the accounts of the Union and the States shall be kept (Article 150).
- CAG also assists the Finance Commission in arriving at a fair understanding of the actual financial position of the states
- Compilation and Maintenance of Accounts of State Governments
- Ensuring Accurate and Reliable Records
Knowledge Box:
|
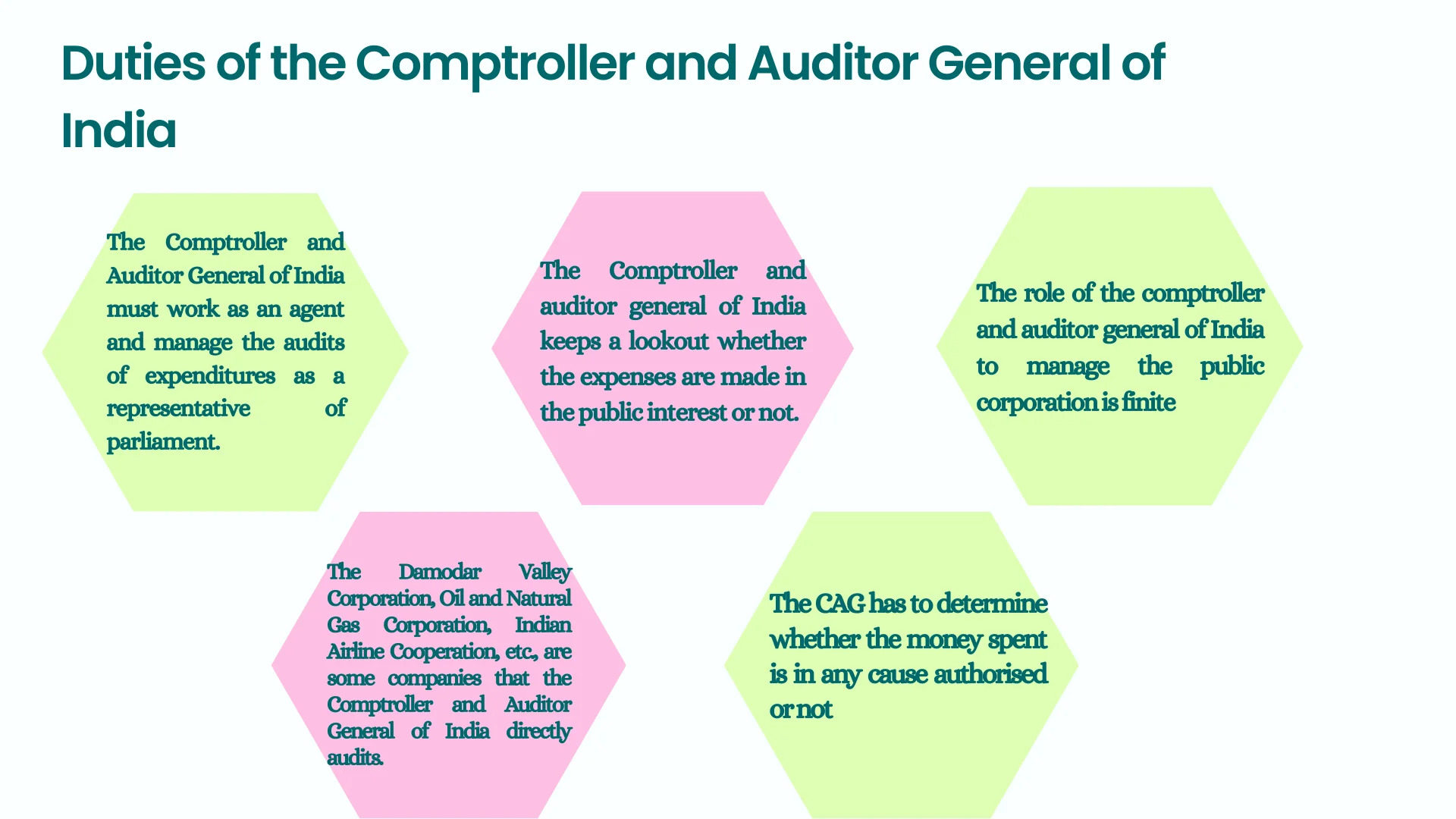
Duties and Power of Comptroller and Auditor General Of India
Article 149 of the Constitution of India mentions the duties and powers of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India.
DPC ACT 1971 The Comptroller and Auditor General (Duties, Powers, and Conditions of Service)
The CAG DPC Act 1971 is an act of Parliament that regulates the duties and powers of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG). The act’s main provisions are as follows:
- Form and Manner of Accounts: The act defines the form and manner of keeping and auditing the accounts of the Union and the States by the CAG.
- Audit of Receipts and Expenditures: The act empowers the CAG to audit the receipts and expenditures of the Union and the States and any authority or body financed by them.
- Audit at Request: The act empowers the CAG to audit the accounts of any body or authority at the request of the President, the Governor, or the State Legislature.
- Local Bodies Accounts: The act empowers the CAG to prescribe and audit the accounts of the local bodies, such as Panchayats and Municipalities.
- Submission of Audit Reports: The act empowers the CAG to submit his audit reports to the President or the Governor, who shall cause them to be laid before the Parliament or the State Legislature.
- Salary: The Comptroller and Auditor-General receives a salary equal to a Supreme Court Judge.
- If they had a pre-existing pension, the salary is reduced by the pension amount or its commuted value.
- Tenure: The term of the Comptroller and Auditor-General is six years, but if they turn sixty-five before completion, they must vacate the office.
- He can resign with written notice to the President.
- Leave: Leave during the tenure is granted to those in prior government service, following relevant rules.
- The President has the authority to grant or deny leave.
- Pension: The individual, previously in government service, is deemed retired upon assuming the role.
- However, their service as Comptroller and Auditor-General count toward pensionable service in their prior category.

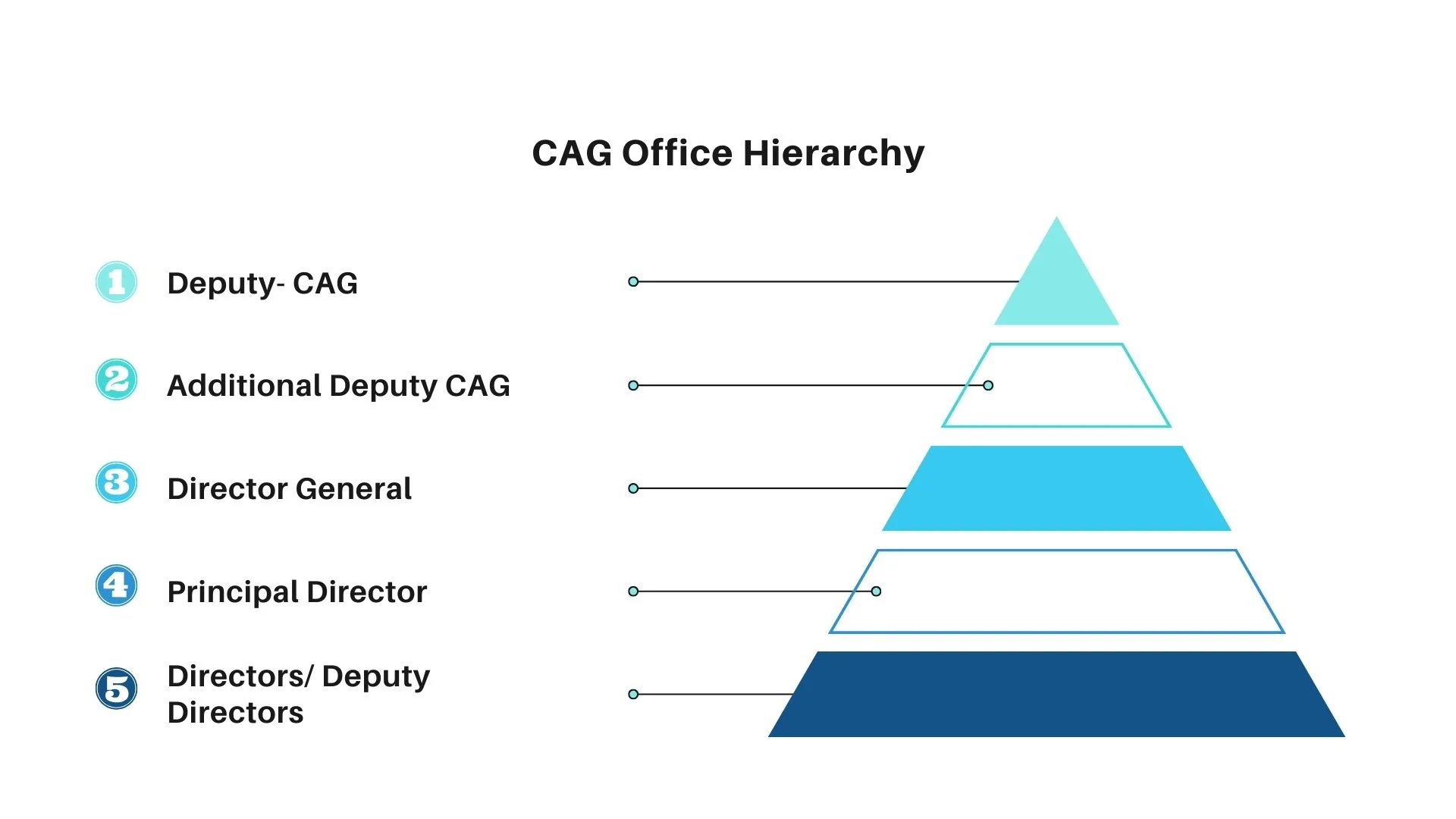
Office of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India
The Comptroller and Auditor General of India leads the Indian Audit and Accounts Department (IAAD).
- Five Deputy Comptroller and Auditors General of India assisted him.
- The Chairperson of the Audit Board is one of the Deputies.
- Four Additional Deputy Comptroller and Auditors General of India are below the Deputy CAG.
- This office’s hierarchy is as follows:
Issues and reforms related to the office of CAG


Recent Update
|
CAG and Public Accounts Committee
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
The CAG serves as a critical constitutional check on government operations, ensuring financial accountability and transparency.
- However, an overzealous audit has also been linked with the issue of policy paralysis through fear of the 3Cs (CBI-CVC-CAG).
- Therefore, reforms aimed at promoting institutional independence and political neutrality are necessary to balance effective oversight with a conducive policy environment.
Constitutional Provisions concerning Duties and Functions of CAG
| Article of the Constitution | Duties and Functions |
| Article 148 |
|
| Article 149 |
|
| Article 150 |
|
| Article 151 |
|
| Article 279 |
|
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Supreme Court | Constitution: A Living Document |
| Contingency Fund of India, Meaning, Corpus and Benefits | Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India – Role & Functions |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









