NITI Aayog, the National Institution for Transforming India, is the premier policy think tank of the Government of India. Established in 2015, it replaced the Planning Commission, adopting a bottom-up approach to policy-making to empower state governments and foster cooperative federalism. NITI Aayog aims to drive economic development and facilitate collaboration between the central and state governments.

Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
NITI Aayog: Pioneering Cooperative Federalism and Inclusive Development in India
Establishment of NITI Aayog:
- Establishment and Status: In response to evolving needs, the Government of India established NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) in 2015, replacing the Planning Commission.
- Consultation and Decision-Making: This decision followed extensive consultations with Chief Ministers, experts, economists, and the general public.
- Objectives and Approach: NITI Aayog aims to better serve the people’s needs and aspirations by fostering cooperative federalism and adopting a bottom-up approach to policy-making, thereby empowering state governments and fostering a collaborative spirit.
- Legal Status: NITI Aayog was established through an executive resolution of the Indian government (Union Cabinet). Thus, it is a non-statutory body (not established by a Parliamentary Act) and an extra-constitutional body (not constituted by the Constitution).
- Vision for India: India aims to fulfill its citizens’ aspirations and stand proudly on the global stage. Progress and improved governance require active participation from the people.
- This transformation involves both planned changes and those driven by market forces and global shifts.
- The maturing of institutions necessitates a redefined role for centralized planning, leveraging the demographic dividend through education, skill development, gender equality, and employment.
- Role of Government: The government’s role in achieving national objectives may evolve, but it remains significant. Policies must reflect and anticipate the country’s needs, integrating global political and economic trends. Effective governance in India will rest on the following pillars:
- Pro-people Agenda: Fulfilling societal and individual aspirations.
- Pro-active Governance: Anticipating and responding to needs.
- Participative Approach: Involving citizens in governance.
- Inclusion: Ensuring all groups are included.
- Equality of Opportunity: Providing equal chances for youth.
- Sustainable Development: Protecting the environment.
- Transparency: Using technology for visible and responsive governance.
- Partnership for Improved Governance: mproving governance requires a synergistic partnership among public, private sectors, and civil society. Effective service delivery depends on active participation at all levels.
- Evolving Institutional Framework: The institutional framework has evolved, necessitating domain expertise for specific functions.
- NITI Aayog serves as the government’s think tank, providing strategic and technical advice on national and international policy issues.
- It replaces the one-way flow of policy from Union to State with a genuine partnership, aiming to find India’s unique strategy for growth.
Need for the Establishment of NITI Aayog
- Challenges Faced by the Planning Commission: The Planning Commission of India, established in 1950, played a crucial role in India’s post-independence development journey.
- However, over time, the Commission’s effectiveness was called into question due to its top-down approach, limited state participation, and lack of innovation.
- Transition to NITI Aayog: To address these shortcomings, the government of India decided to replace the Planning Commission with a new institution that would adopt a more inclusive and collaborative approach to policymaking.
- Thus, NITI Aayog, the National Institution for Transforming India, came into existence in 2015.
Key Objectives of Establishing NITI Aayog
- Cooperative Federalism: NITI Aayog was envisioned to foster a more cooperative federalism, where the central government and state governments work together in a spirit of partnership to address India’s development challenges.
- Bottom-Up Approach: Unlike the Planning Commission’s top-down approach, NITI Aayog emphasizes bottom-up planning, giving more autonomy and decision-making power to state governments and local bodies.
- Think Tank Role: NITI Aayog functions as a premier policy think tank, providing strategic advice and innovative solutions to the government on a wide range of issues, including economic policy, social policy, infrastructure development, and environmental sustainability.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: NITI Aayog actively monitors and evaluates the implementation of government programs and initiatives, ensuring that they are aligned with national goals and objectives.
- Sustainable Development: NITI Aayog plays a key role in promoting sustainable development practices, ensuring that India’s growth trajectory is environmentally responsible and socially inclusive.
Key Principles of NITI Aayog
- Empowering States as Equal Partners: Empowering states as equal partners in national development, emphasizing the concept of Cooperative Federalism.
- Knowledge Center for Governance: Serving as a knowledge center for both internal and external resources, acting as a repository of best governance practices and functioning as a Think Tank that provides specialized knowledge, strategic expertise, and technical advice to all levels of government.
- Collaborative Platform for Development: Establishing a collaborative platform that facilitates the implementation of development initiatives, monitors progress, addresses shortcomings, and brings together various ministries at the national and state levels to pursue developmental objectives jointly.
Composition
- Niti Aayog is chaired by Hon’ble Prime Minister of India. It also includes following :
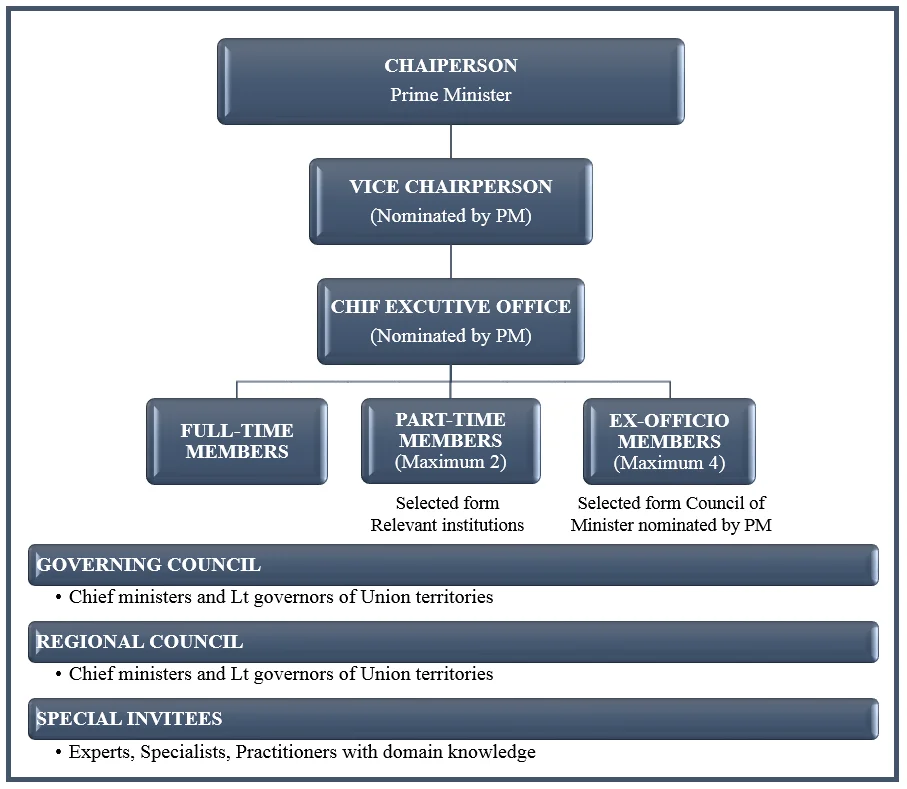
The NITI Aayog, which is a government organization in India, has the following structure:
- Chairperson: The head of NITI Aayog is the Prime Minister of India.
- Governing Council: This council includes the Chief Ministers of all Indian states, the Chief Ministers of Union Territories with their own legislatures (such as Delhi, Puducherry, and Jammu and Kashmir), and the Lt.
- Governors of other Union Territories.

- Regional Councils: These councils are set up to address specific issues that affect more than one state or region.
- They are temporary and convened by the Prime Minister.
- Members include the Chief Ministers of states and Lt. Governors of Union Territories in the respective region.
- The Chairperson of NITI Aayog or their nominee chairs these councils.
- Special Invitees: Experts, specialists, and practitioners with relevant knowledge are invited by the Prime Minister to provide their expertise.
- Full-time Organizational Framework:
- Vice-Chairperson: Appointed by the Prime Minister, with the rank of a Cabinet Minister.
- Members: Full-time members with the rank of a Minister of State.
- Part-time Members: A maximum of 2 members from leading universities, research organizations, and relevant institutions, serving in an ex-officio capacity. These members serve on a rotation.
- Ex-Officio Members: Up to 4 members of the Union Council of Ministers nominated by the Prime Minister.
- Chief Executive Officer: Appointed by the Prime Minister for a fixed term, holding the rank of Secretary to the Government of India.
- Secretariat: Staff members considered necessary to support the functioning of NITI Aayog.
Specialized wings
- Research Wing: It develops in-house sectoral expertise as a dedicated think tank of top-notch domain experts, specialists, and scholars.
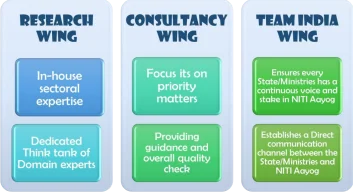
- Consultancy Wing: It provides a marketplace of vetted panels of expertise and funding for the Central and State Governments to tap into matching their requirements with solution providers, public and private, national and international.
- By playing matchmaker instead of providing the entire service, NITI Aayog can focus its resources on priority matters, providing guidance and an overall quality check to the rest.
- Team India Wing: It includes representatives from every state and ministry and serves as a permanent platform for national collaboration.
- Each Representative:
- Ensures that every State/Ministry has a continuous voice and stake in the NITI Aayog.
- Establish a direct communication channel between the State/Ministry and NITI Aayog as the dedicated liaison interface for all development-related matters.

Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
NITI Aayog serves as a dynamic institution driving India’s development with a focus on collaboration, innovation, and sustainable practices.
- By empowering states and acting as a central knowledge hub, it aims to transform India’s policy-making landscape for more effective governance and inclusive growth.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| NITI Aayog | Planning Commission and India’s Five-Year Plans |
| Cooperative Federalism in India: Significance, Background & Importance | Prime Minister of India |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program










