NITI Aayog, established in 2015, plays a vital role in India’s development by promoting cooperative federalism and effective governance. It has two key offices: the National Institute of Labour Economics Research and Development (NILERD) and the Development Monitoring and Evaluation Office (DMEO), which support its mission. NITI Aayog focuses on empowering states, fostering inclusive growth, and addressing socio-economic inequalities, all while emphasizing the importance of collaboration at various governance levels.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Empowering States: The Role of NITI Aayog in India’s Governance
Attached Offices
The Role of NILERD and DMEO in NITI Aayog
- The NITI Aayog has two affiliated offices, which are detailed as follows:
- National Institute of Labour Economics Research and Development (NILERD):
- Formerly known as the Institute of Applied Manpower Research (IAMR), the NILERD is an autonomous institution under the NITI Aayog. Its core objectives encompass
- Research, data collection, education
- Training in various facets of human capital planning
- Human resource development, and monitoring and evaluation.
- Foundation and Purpose: IAMR was founded in 1962 in accordance with the Societies Registration Act of 1860 with the purpose of acting as a hub for ideas and policy research pertaining to the development of human capital.
- It was renamed NILERD in 2014.
- Funding Sources: The primary source of funding for this institute is grants-in-aid from the NITI Aayog, which is augmented by income from research projects, education and training programs.
- Main Goals: The main goal of NILERD is to provide an institutional structure that can support and direct a systematic applied research process in human resource planning.
- Academic Excellence: Over the years, NILERD has demonstrated excellence in academic pursuits, particularly in the areas of public policy and program monitoring and evaluation, as well as human resource planning and development.
- Campus Relocation: In 2002, the institute moved to its dedicated campus in Narela, an expanding institutional and urban hub recognized as a knowledge-focused special economic zone in the National Capital Region.
- Development Monitoring and Evaluation Office (DMEO):
-
- The DMEO was established by the Indian Government in 2015 as an attached office of the NITI Aayog, consolidating the former Programme Evaluation Organization and the Independent Evaluation Office.
- Headed by the Director General, who holds a position equivalent to an Additional Secretary to the Government of India, the DMEO operates independently with separate budget allocations and manpower, ensuring functional autonomy. In addition to the Director General, the DMEO has four Deputy Director Generals to carry out the mandate and a Joint Secretary to provide administrative and logistics support.
- The DMEO is tasked with actively monitoring and evaluating the implementation of Government of India programs and initiatives, including identifying the necessary resources to enhance the likelihood of success and the scope of delivery.
- Its functions include –
-
- monitoring government programs
- assisting ministries in designing Terms of Reference (TORs) for evaluation studies
- tracking the progress of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs),
- fostering cooperative federalism
- conducting evaluations of government programs.
Objectives and Functions of NITI Aayog
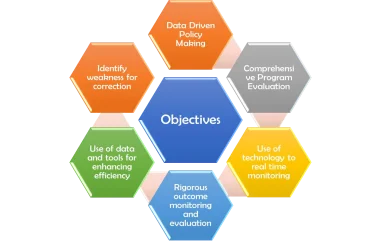
The NITI Aayog aims to enable India to better face complex challenges through the following:
- Harnessing Demographic Dividend: Leveraging India’s demographic dividend and realization of the potential of youth, men, and women through education, skill development, elimination of gender bias, and employment.
- Promoting Cooperative Federalism: Promote cooperative federalism by providing ongoing support and structured mechanisms to States, recognizing that strong States contribute to a robust nation.
- Economic Strategies and National Security: Ensure that economic strategies and policies consider national security interests in specific areas referred to it
- Inter-sectoral and Inter-departmental Collaboration: Serve as a platform for resolving inter-sectoral and inter-departmental issues, expediting the implementation of the development agenda.
- Poverty Elimination: Elimination of poverty and the chance for every Indian to live a life of dignity and self-respect.
- Addressing Inequalities: Redressal of inequalities based on gender bias, caste, and economic disparities.
- Integrating Villages in Development: Integrate villages institutionally into the development process.
- To formulate a mechanism for developing credible plans at the village level.
- Supporting Small Businesses: Policy support to more than 50 million small businesses, which are a major source of employment creation.
- Environmental Protection: Safeguarding our environmental and ecological assets.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Actively monitoring and evaluating the implementation of programmes and initiatives
- Technological Upgradation and Capacity Building: Focus on technology upgradation and capacity building for implementation of programmes and initiatives to enable an administration paradigm shifts from “a provider of first and last resort” to “an enabler.”
- Innovation and Entrepreneurial Support: Create an innovation and entrepreneurial support system through collaboration of national and international experts.
- Resource Centre for Best Practices: Maintain a state-of-the-art Resource Centre to be a repository of good governance and best practices for sustainable and equitable development.
NITI Aayog focuses on thematic policy interventions to achieve its objectives through vertical cells. Following are the vertical cells:
Guiding Principles Of NITI Aayog
- Antyodaya: upliftment of marginalized sections of society.
- Inclusion: addressing inequalities based on gender, caste, religion, region or class.
- People’s participation: in the developmental process to ensure a participative citizenry.
- Village: to ensure grassroots-level participation in the development process.
- Good Governance: shift the focus of government policies from outlay to output to outcome. Maintain a transparent, accountable, and proactive style of governance.
- Sustainability: of our planning and development process.
- Demographic dividend: harnessing the gift of a large proportion of the working-age population through education, skill development, and productive livelihood opportunities.
Seven Pillars of Effective Governance
NITI Aayog is based on the following seven pillars of effective governance:
- Pro-People agenda that fulfills the aspirations of the society and individuals as well.
- Proactive in anticipating and responding to citizen needs.
- Participative, by involvement of citizens.
- Empowering women in all aspects.
- Inclusion of all groups with a special focus on SCs, STs, OBCs, and minorities.
- Equality of opportunity for the youth.
- Transparency through technology to make the government visible and responsive.
NITI AAYOG HAS HELPED IN REDEFINING FEDERALISM
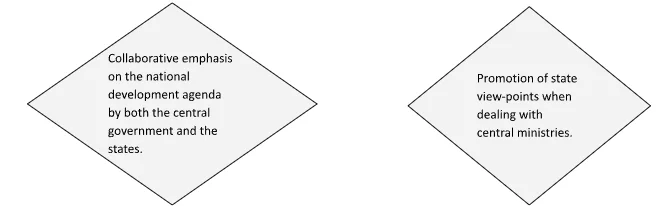
- NITI Aayog’s Role in Collaborative Federalism: Establishing the NITI Aayog helped to realize the crucial objective of fostering collaborative federalism and promoting effective governance in India. Its purpose is to empower robust state governments, contributing to the overall strength of the nation.
- Key Aspects of Cooperative Federalism: The two key aspects of Cooperative Federalism are –
- Village-Level Planning and Aggregation: Help states to develop mechanisms to formulate credible plans at the village level and aggregate these progressively at higher levels of government.
- Fostering Cooperative and Competitive Federalism: It is fostering a sense of cooperative federalism along with competitive federalism by releasing rankings on various development parameters like health, education, and water management, etc.
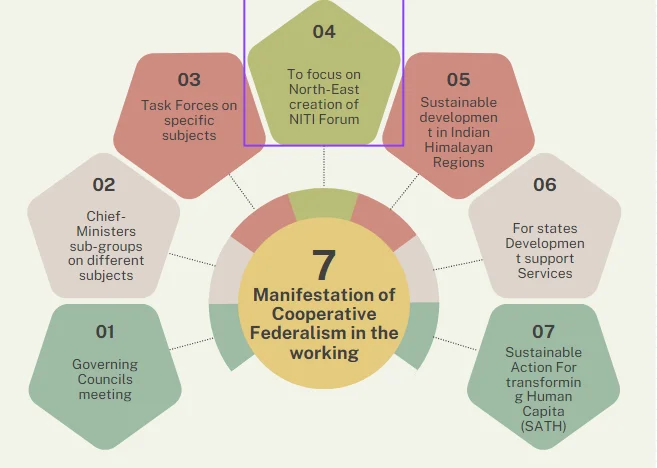
- Addressing Regional Development Imbalances: With the aim of correcting regional development imbalance, it has taken special steps for regions needing special attention and support, like the North Eastern States, Island States, and hilly Himalayan States by constituting special forums to identify their specific constraints.
- Formulating special policies to ensure sustainable development takes place in these regions while also protecting their abundant natural resources.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
NITI Aayog has redefined India’s approach to federalism by encouraging states to participate actively in development planning.
- Its focus on collaboration, monitoring, and evaluation helps ensure that government initiatives effectively meet the needs of the people.
- By prioritizing sustainable development and inclusivity, NITI Aayog aims to build a stronger and more equitable India for all its citizens.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| NITI Aayog | Federalism |
| Cooperative Federalism in India: Significance, Background & Importance | Empowering Marginalized Communities: Upholding Democratic Rights for Equality |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program